ROUTE 53 - GLOBAL DNS
R53 Hosted Zones
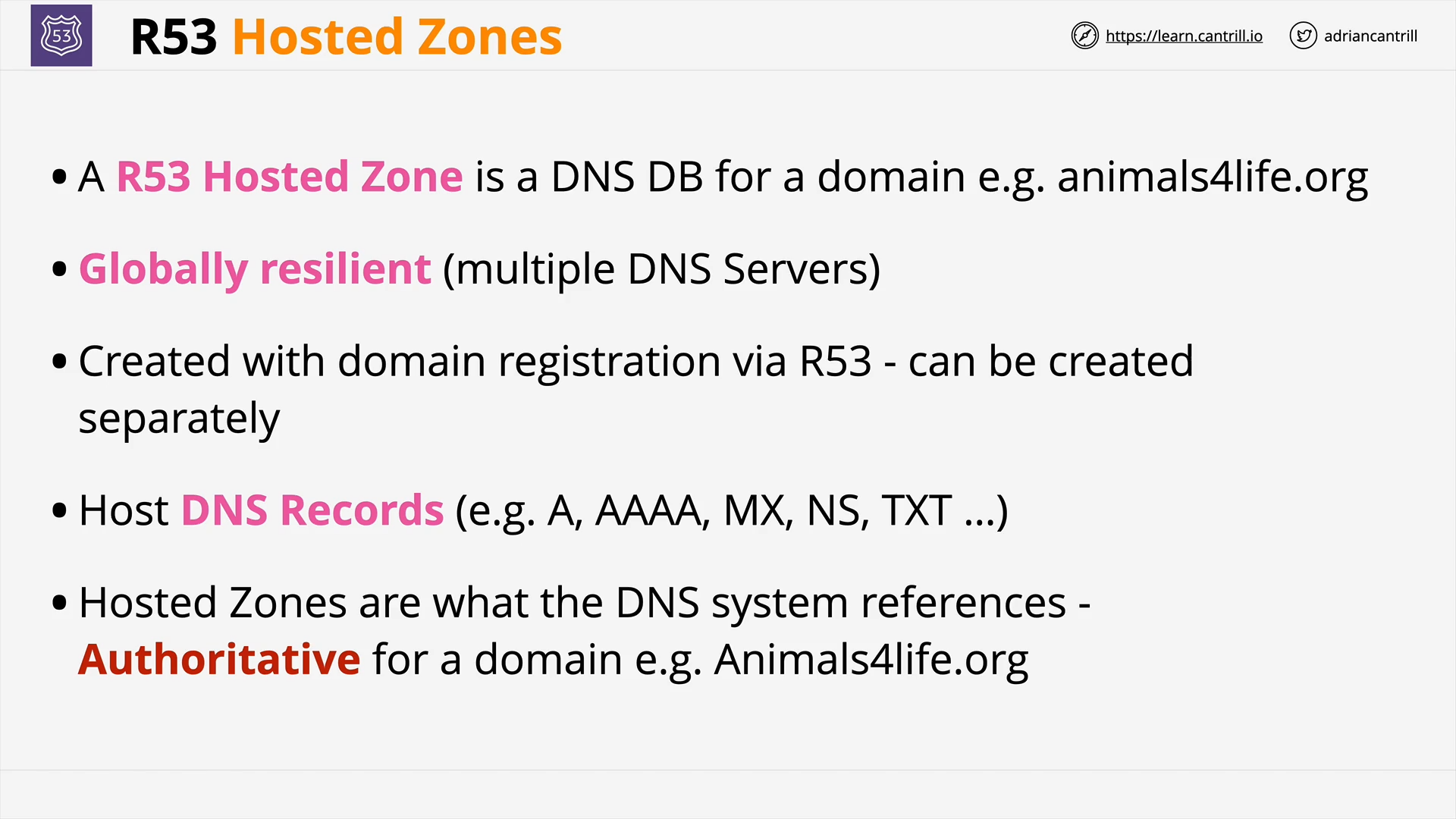
what is a route53 hosted zone?
A DNS database for a domain, e.g. animals4life.io
- It’s what the DNS system references for a domain.
- In other words, hosted zone is the Authoritative nameserver of a domain.
R53 Public Hosted Zones (6:28)
 R53 Public Hosted Zones - Overview
R53 Public Hosted Zones - Overview
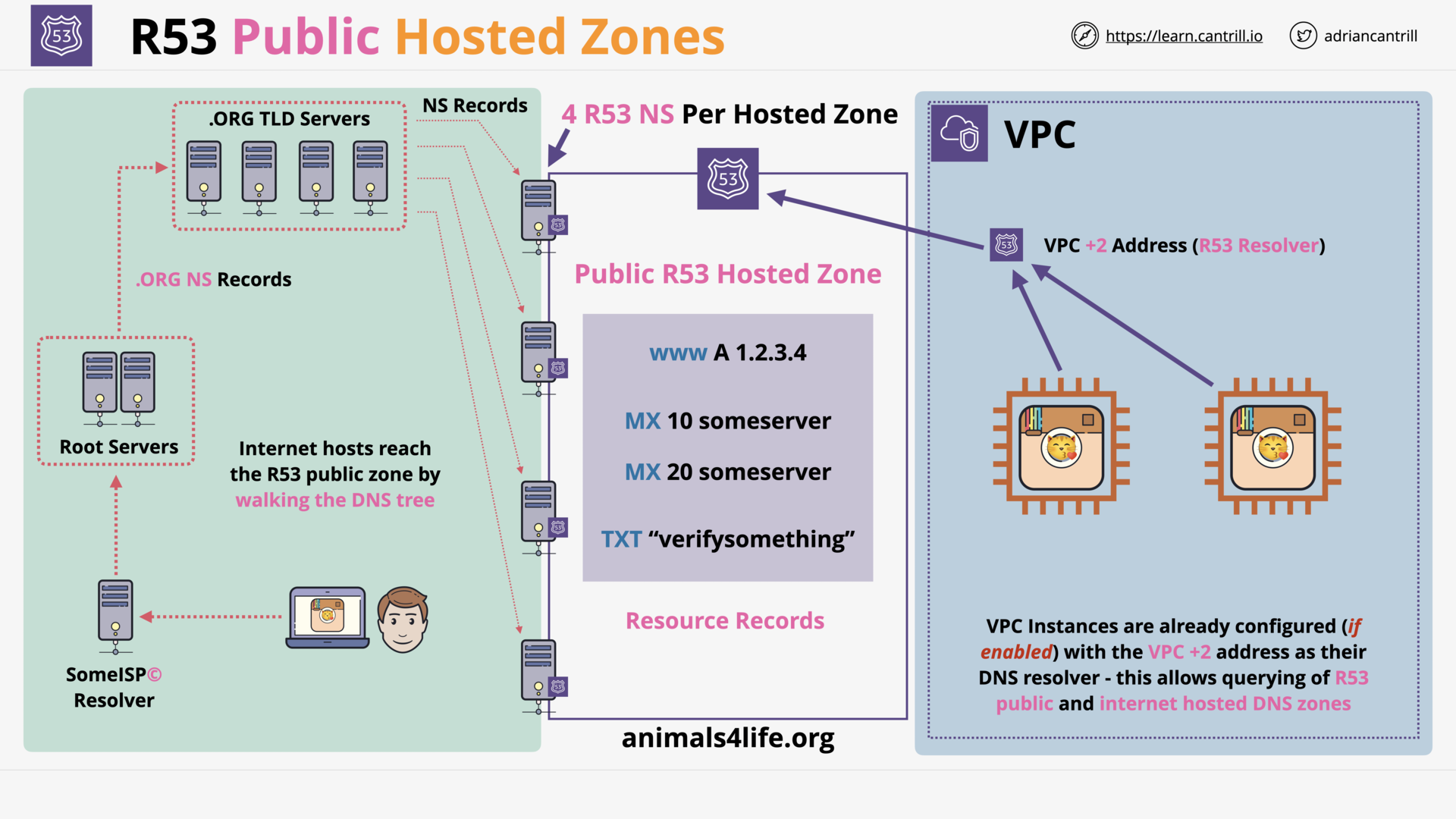
how many nameservers does a public hosted zone have?
4 Route53 nameservers
what is the accessibility of a r53 public zone?
A R53 Public Zone can be accessed from:
- the public internet
- AWS VPCs.
for a public hosted zone, what is the dns query process of the aws vpc?
- VPC Instances are configured with the VPC
+2 Address(R53 Resolver). - Any resources in the VPC can query public DNS and R53 Public Hosted Zones record.
 R53 Public Hosted Zones - Example
R53 Public Hosted Zones - Example
R53 Private Hosted Zones (5:10)
 R53 Private Hosted Zones - Overview
R53 Private Hosted Zones - Overview
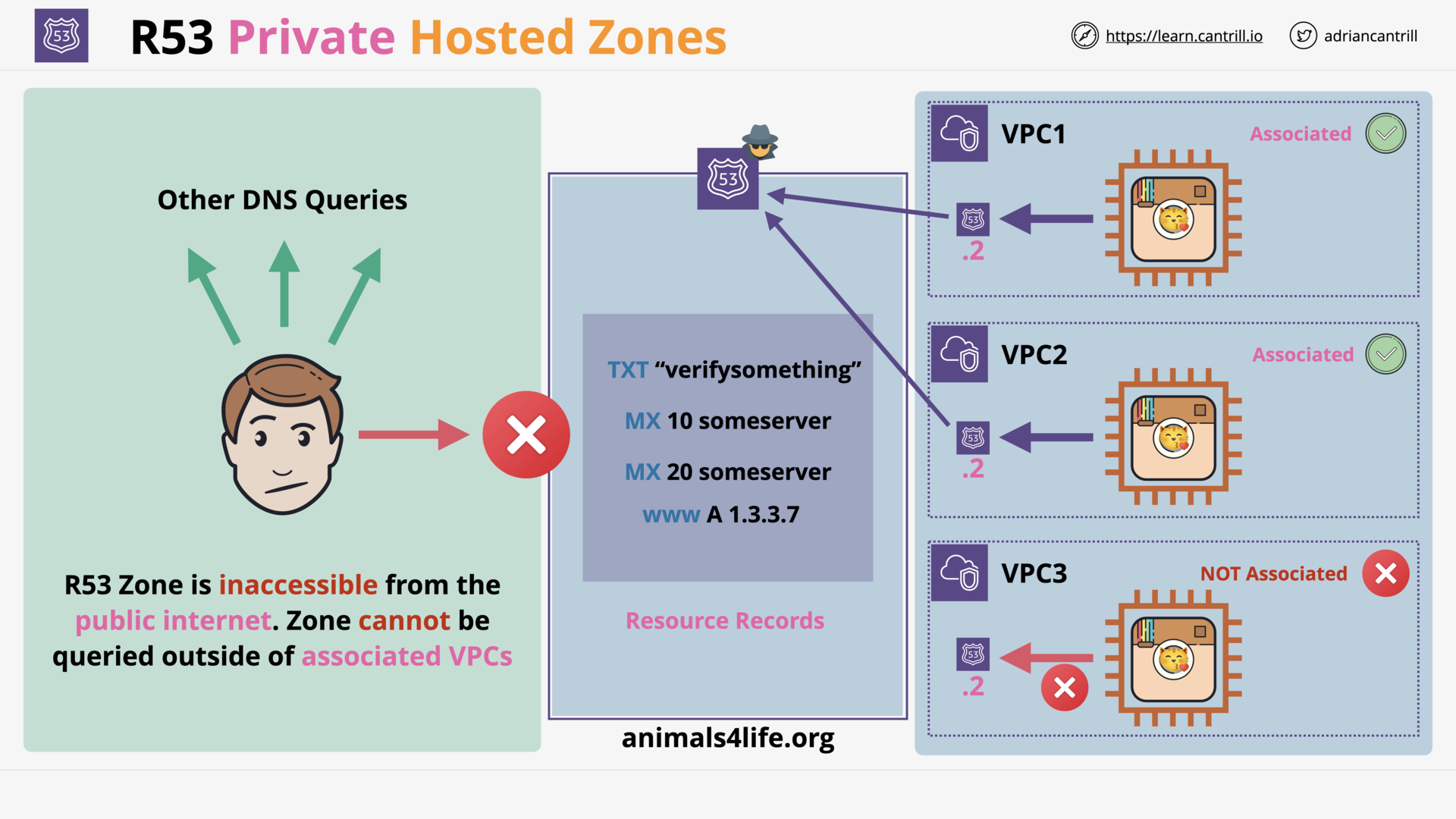
what is the accessibility of a r53 private hosted zone?
A R53 Private Hosted Zone can only be accessed by the VPCs (which with it is associated).
- These VPCs can be from the same account or different accounts.
- The public internet cannot access R53 Private Hosted Zones.
 R53 Private Hosted Zones - Example
R53 Private Hosted Zones - Example
R53 Split View Hosted Zones
 R53 Split View Hosted Zones
R53 Split View Hosted Zones
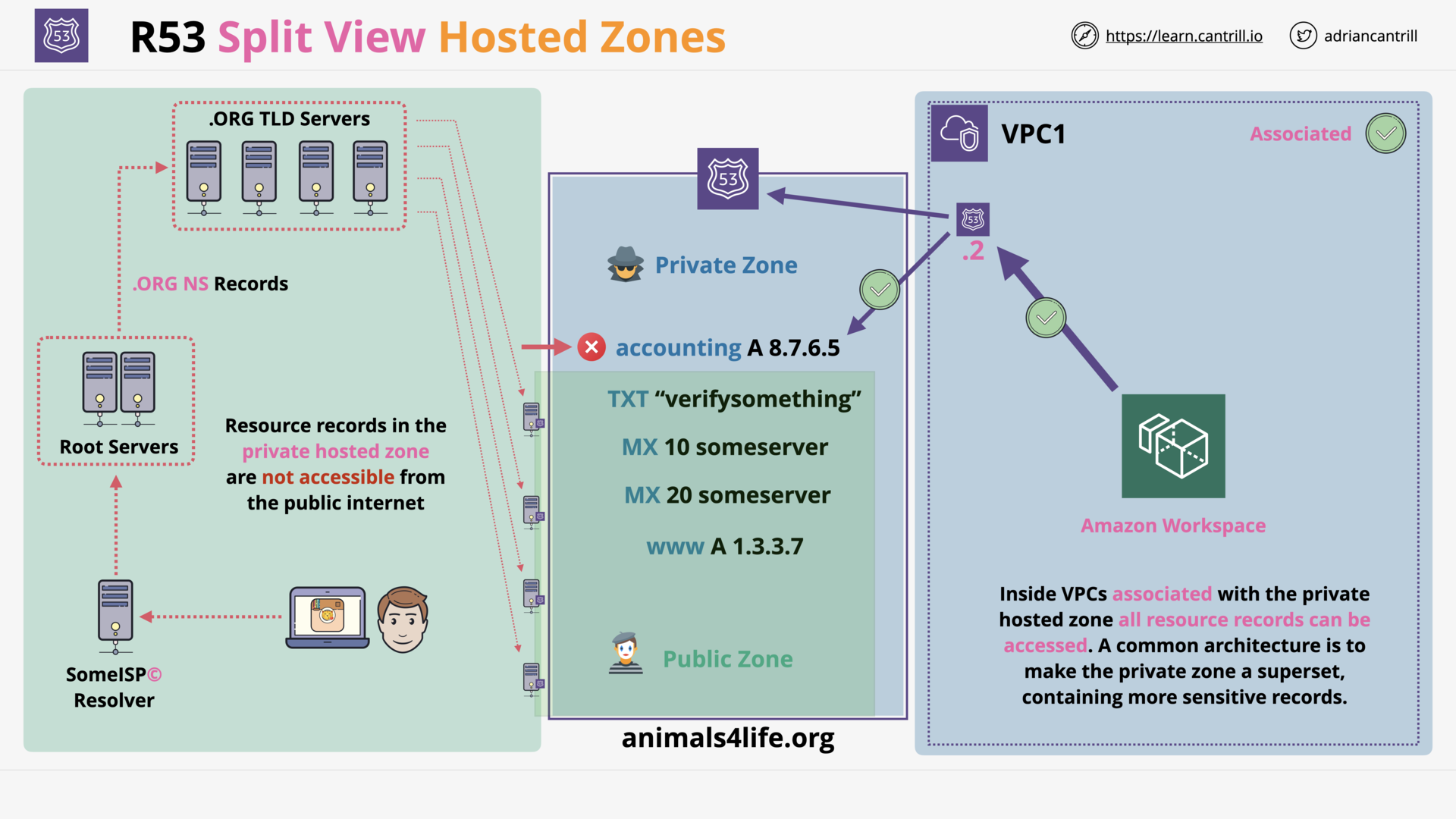
what is r53 split-view dns?
Using the same domain name (example.com) for
- internal uses (
accounting.example.com) - external uses, such as your public website (
www.example.com)
Or even using the same sub-domain for both public (external) and internal usage.
CNAME vs R53 Alias (5:19)

CNAME record - Problem
what is `cname` record?
A CNAME record:
- maps DNS queries for the name of the current record, such as
acme.example.com - to:
- another domain (
example.comorexample.net) - or subdomain (
acme.example.comorzenith.example.org).
- another domain (
 R53
R53 alias record
what is `alias` record?
Amazon Route 53 alias record is a Route 53–specific extension to DNS functionality.
what does r53 `alias` record do?
R53 alias record:
-
route traffic to selected AWS resources, such as
- CloudFront distributions
- Amazon S3 buckets.
-
route traffic from one record in a hosted zone to another record.
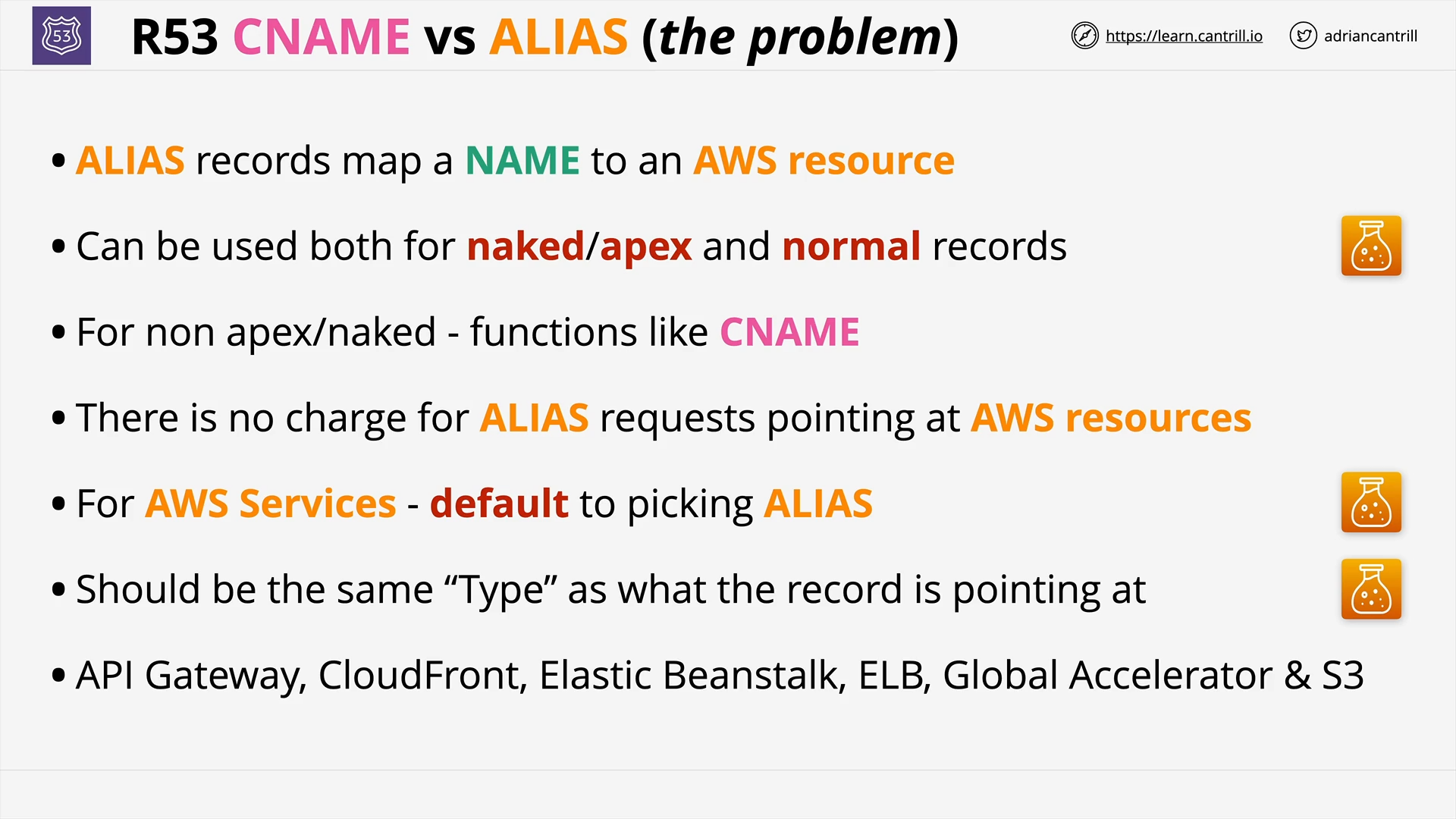
why use r53 `alias` record?
-
Unlike a CNAME record, we can create an R53
aliasrecord at the top node of a DNS namespace, also known as thezone apex.e.g. DNS name
example.com:- We can’t create a
CNAMErecord forexample.com - But we can create a R53
aliasrecord forexample.comthat routes traffic towww.example.com.
- We can’t create a
-
We can use a R53
aliasrecord to route traffic to many AWS resources.Many AWS resources don’t have a static IP address. They only have a DNS name, e.g.
lb1-1234.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.comWith R53
aliasrecord, we can route directly traffic to these DNS name, without allocating an additional Elastic IP address.
Simple Routing (2:17)
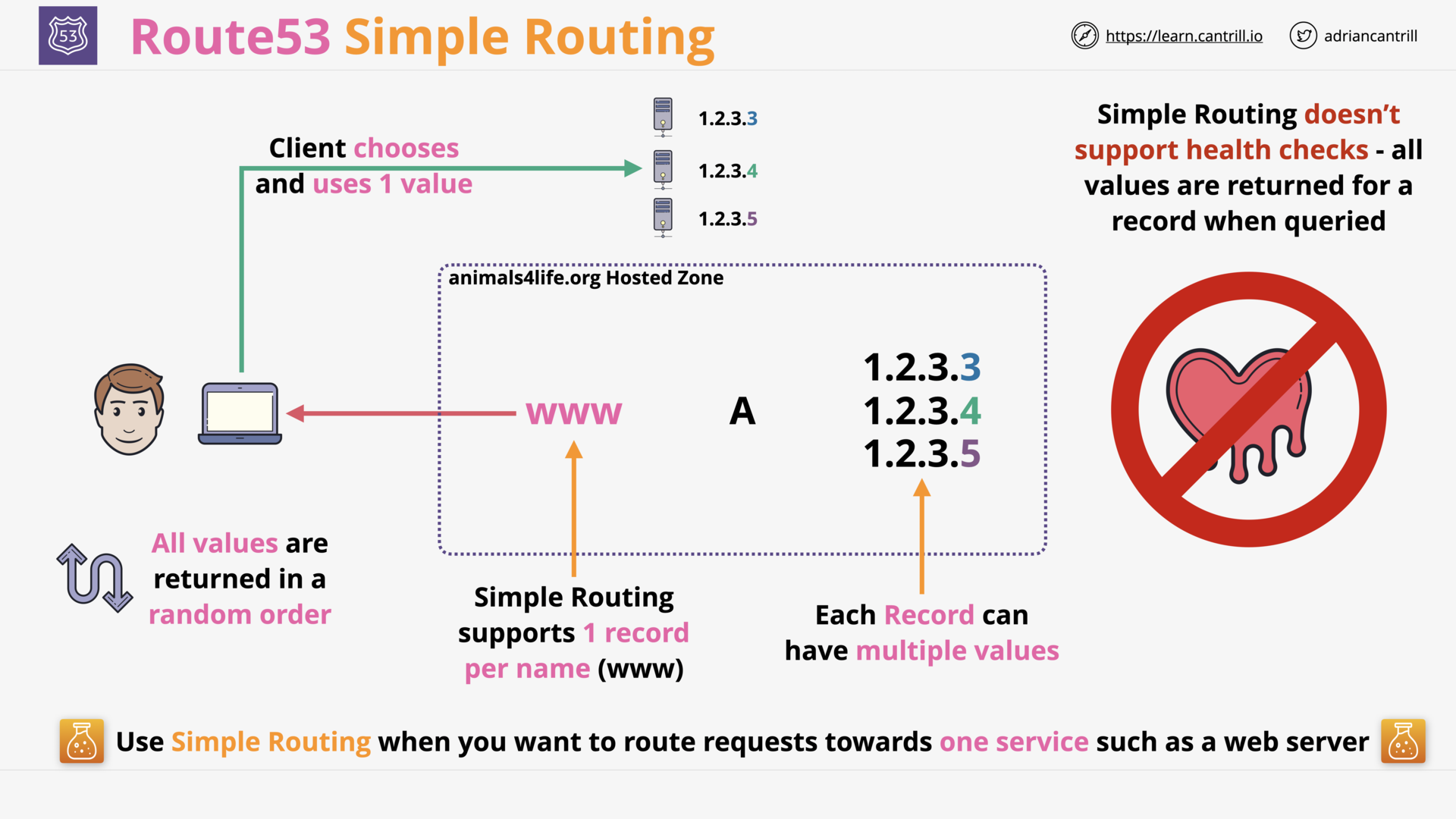
what is r53 `simple routing`?
Routing traffic to a single resource, for example, to a web server for your website.
what is the drawback of r53 `simple routing`?
Simple Routing doesn’t support health check.
R53 Health Checks (12:41)
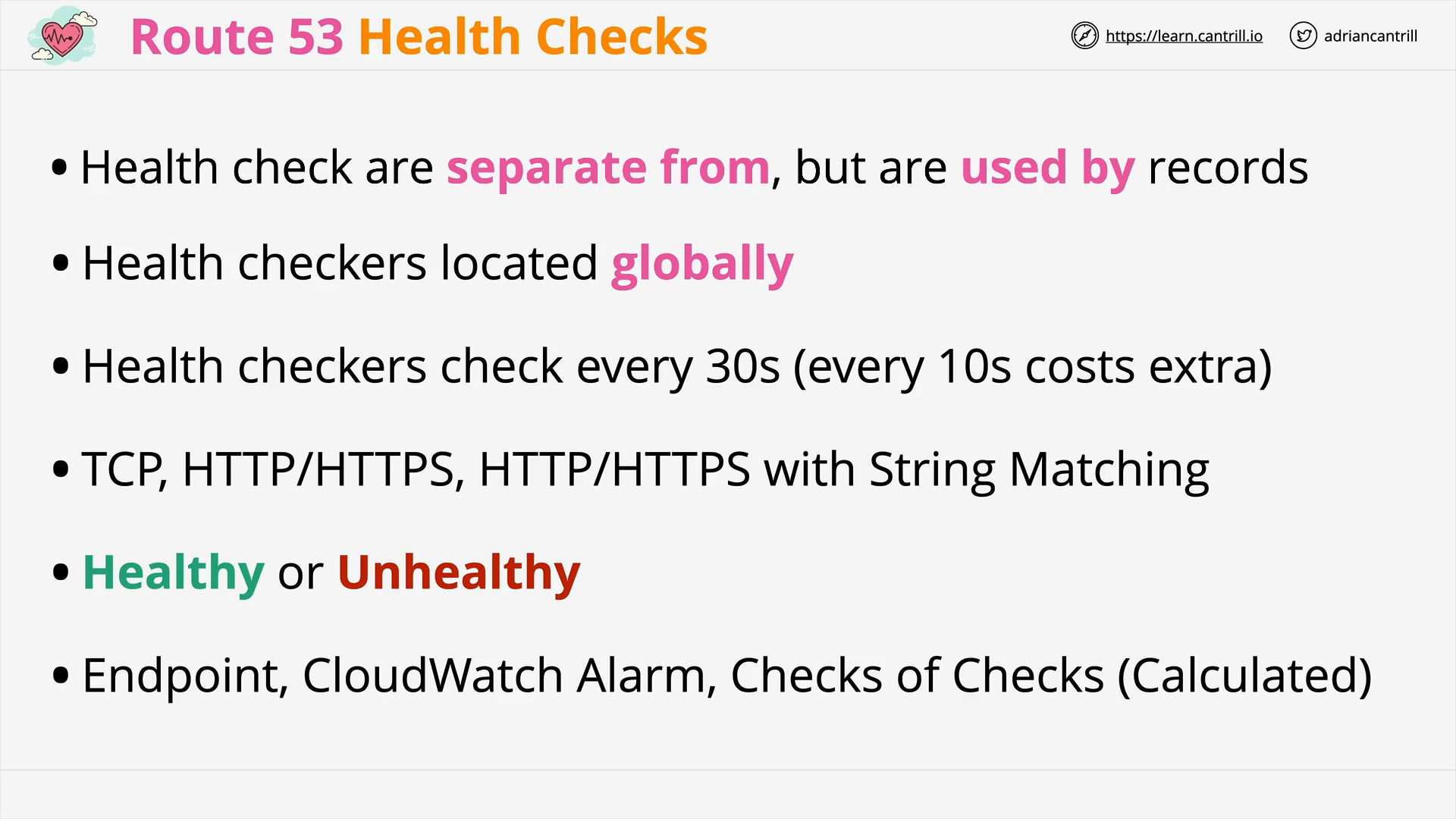 R53 Health Check - Overview
R53 Health Check - Overview
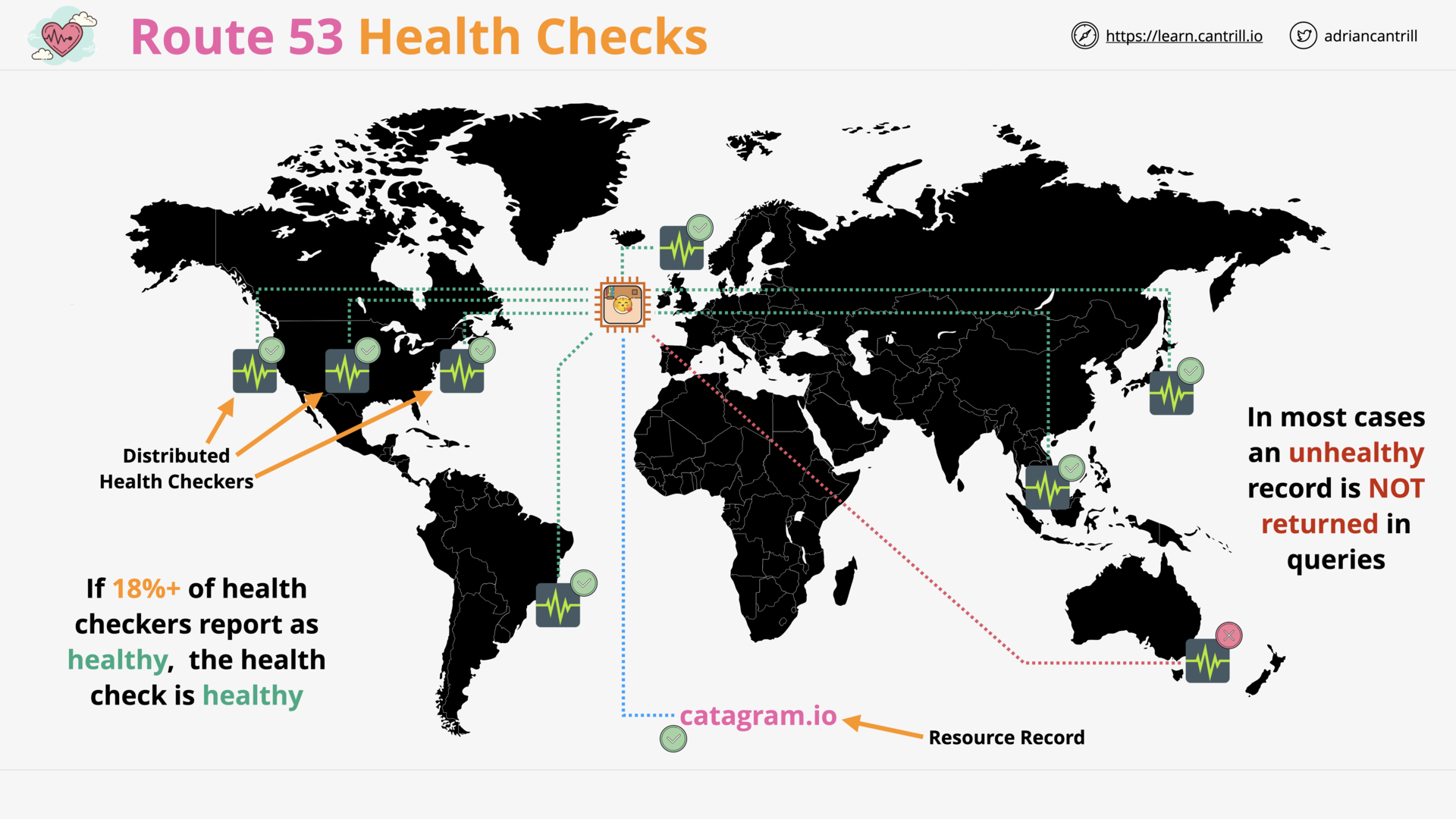 R53 Distributed Health Checkers
R53 Distributed Health Checkers
Failover Routing (1:53)
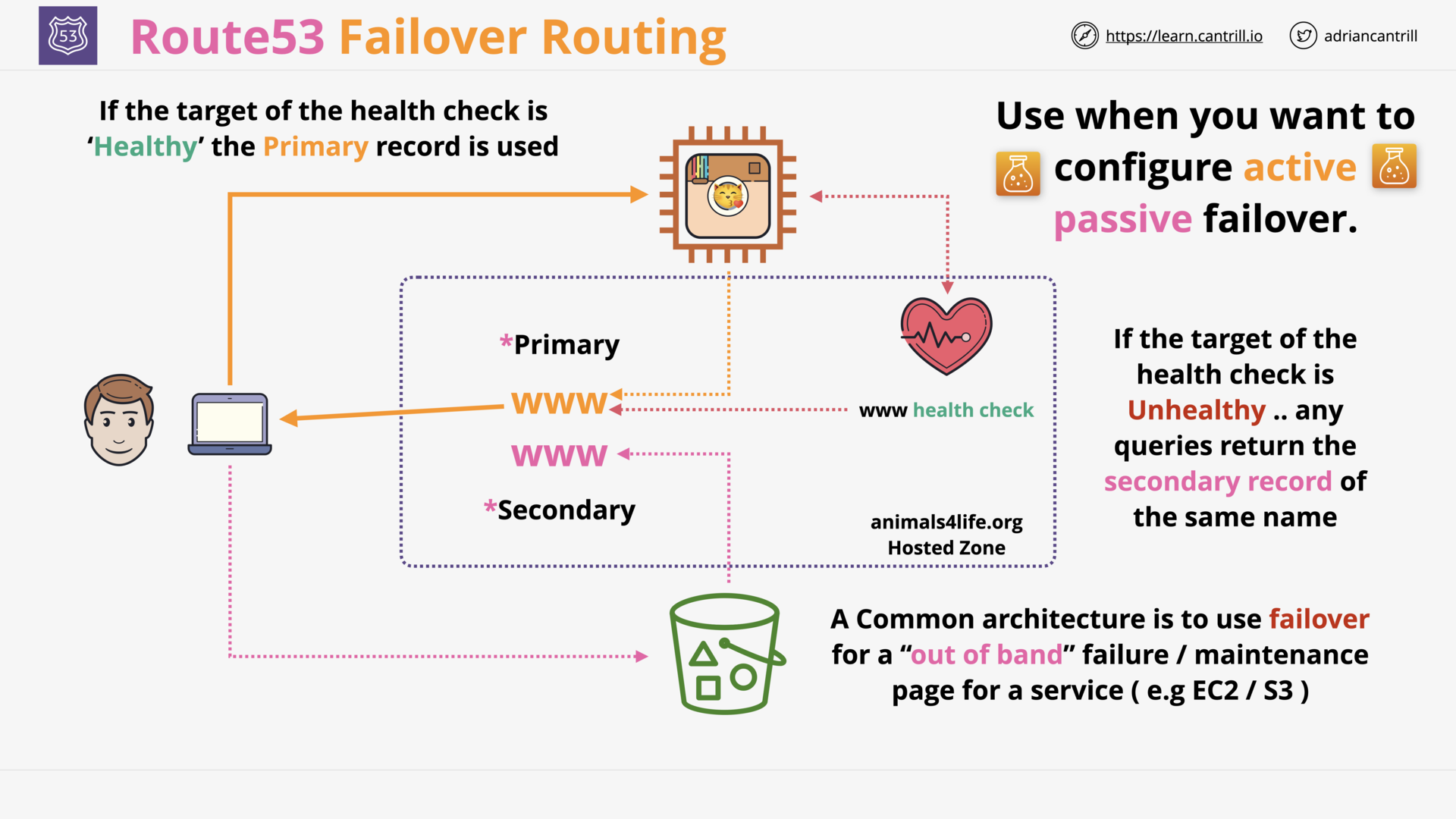 R53 Failover Routing
R53 Failover Routing
what is `failover routing`?
Routing traffic
- to a resource when the resource is healthy
- or to a different resource when the first resource is unhealthy
[DEMO] Using R53 and Failover Routing-PART1 (16:41)
[DEMO] Using R53 and Failover Routing-PART2 (6:28)
Multi Value Routing (2:32)
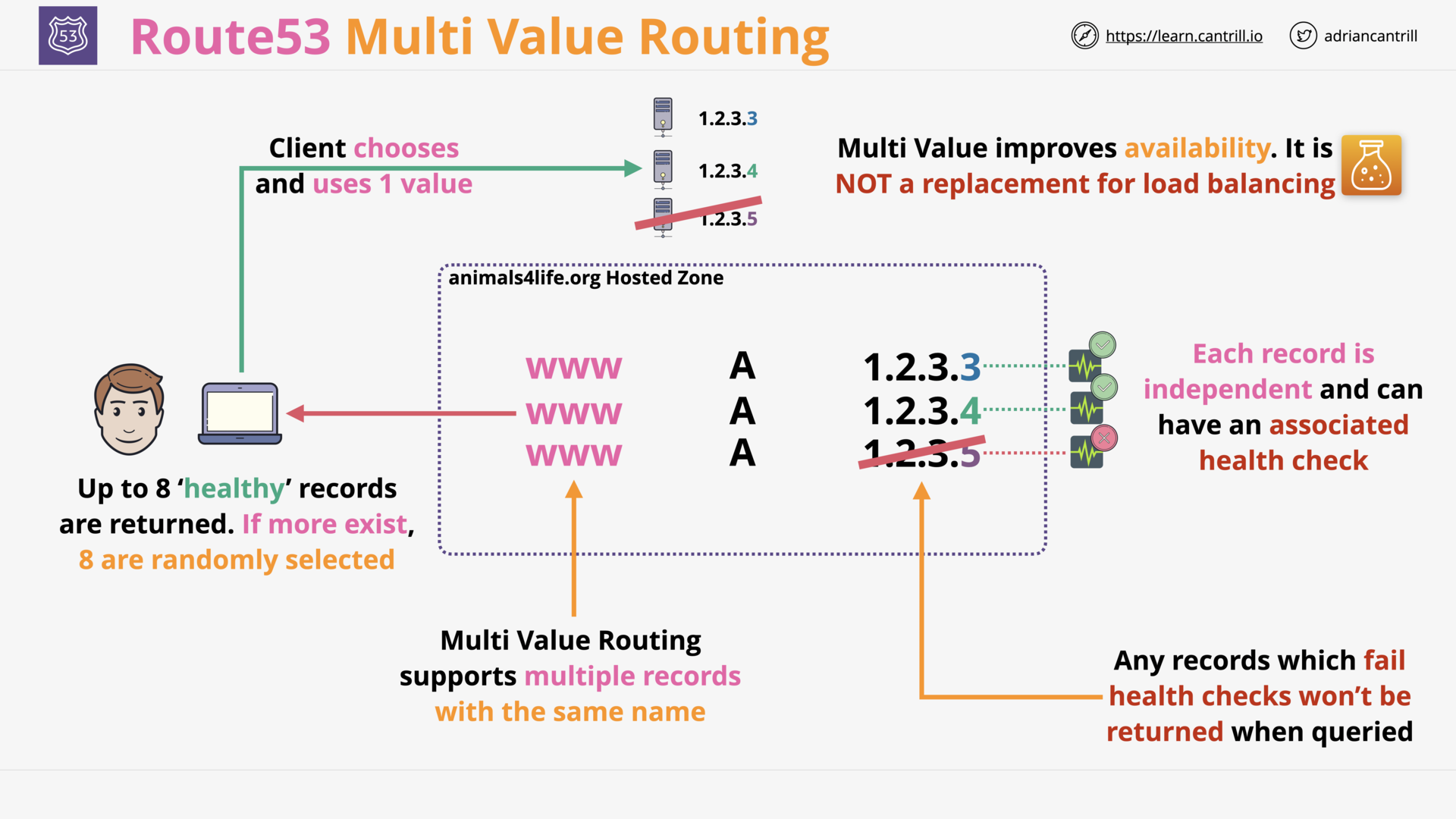 R53 Multi Value Routing
R53 Multi Value Routing
can r53 `simple routing` return multi values?
Yes.
what is the different between `simple routing` and `multi value routing`?
- With
Simple Routing, a hosted zone can have a record that have multi values. - With
Multi Value Routing, a hosted zone can have multiple records with the same name
Weighted Routing (3:24)
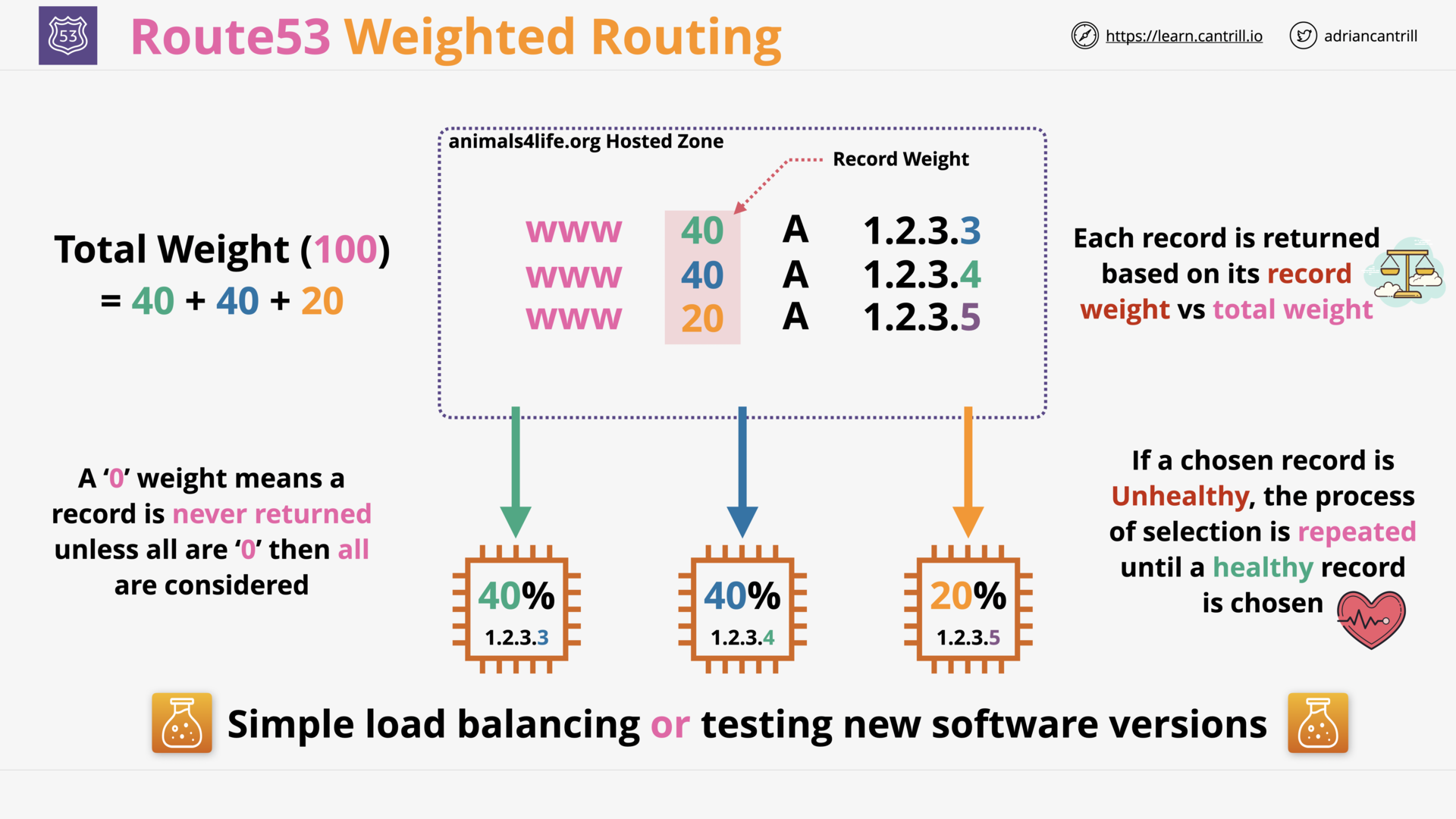 R53 Weighted Routing
R53 Weighted Routing
what is weighted routing?
Associating multiple resources with
- a single domain name (example.com)
- or subdomain name (acme.example.com) and
and choose how much traffic is routed to each resource.
Latency-based Routing (2:44)
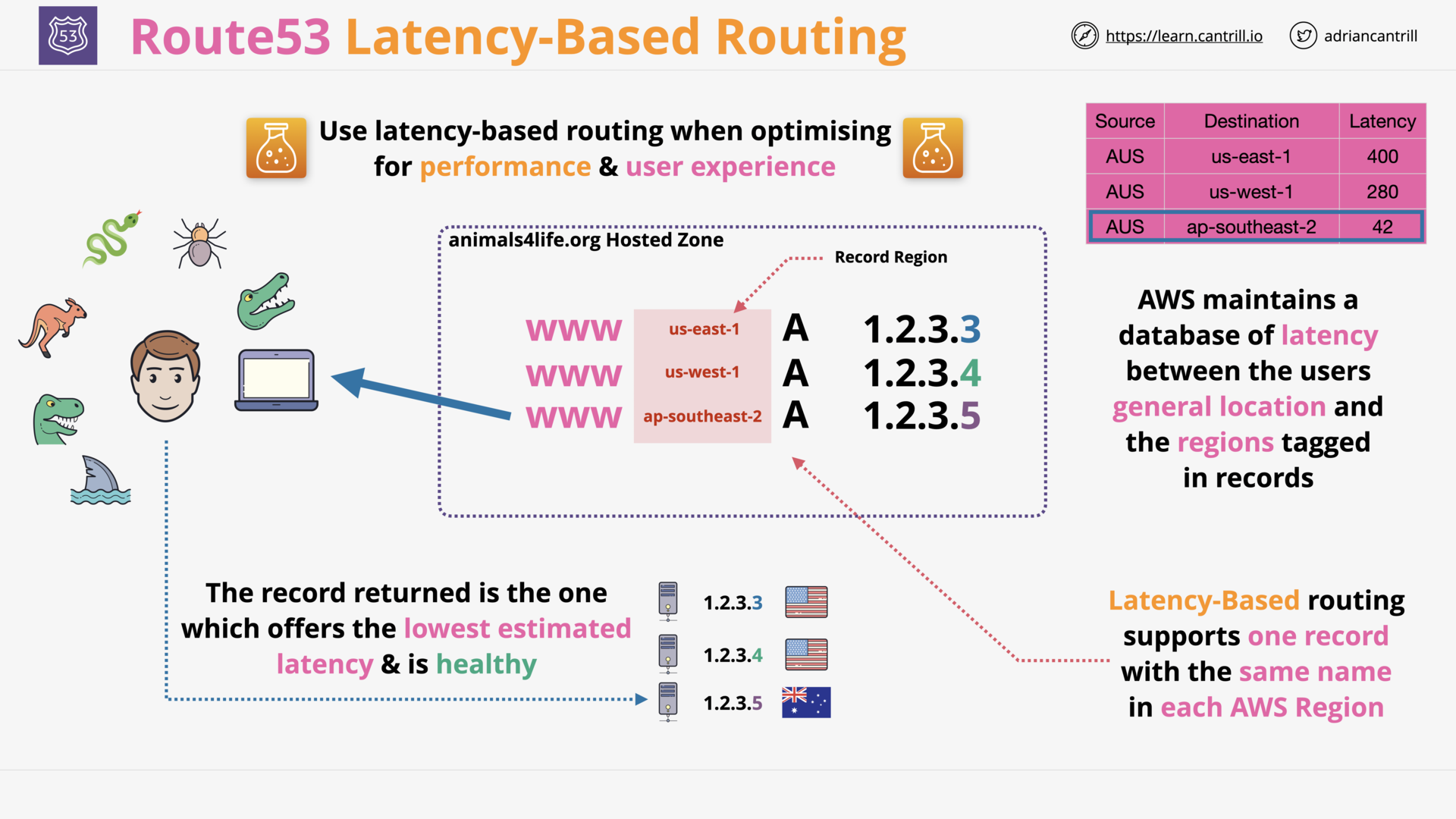
what is latency-based routing?
Routing traffic to the AWS Region that provides the lowest latency.
Geolocation Routing (5:02)
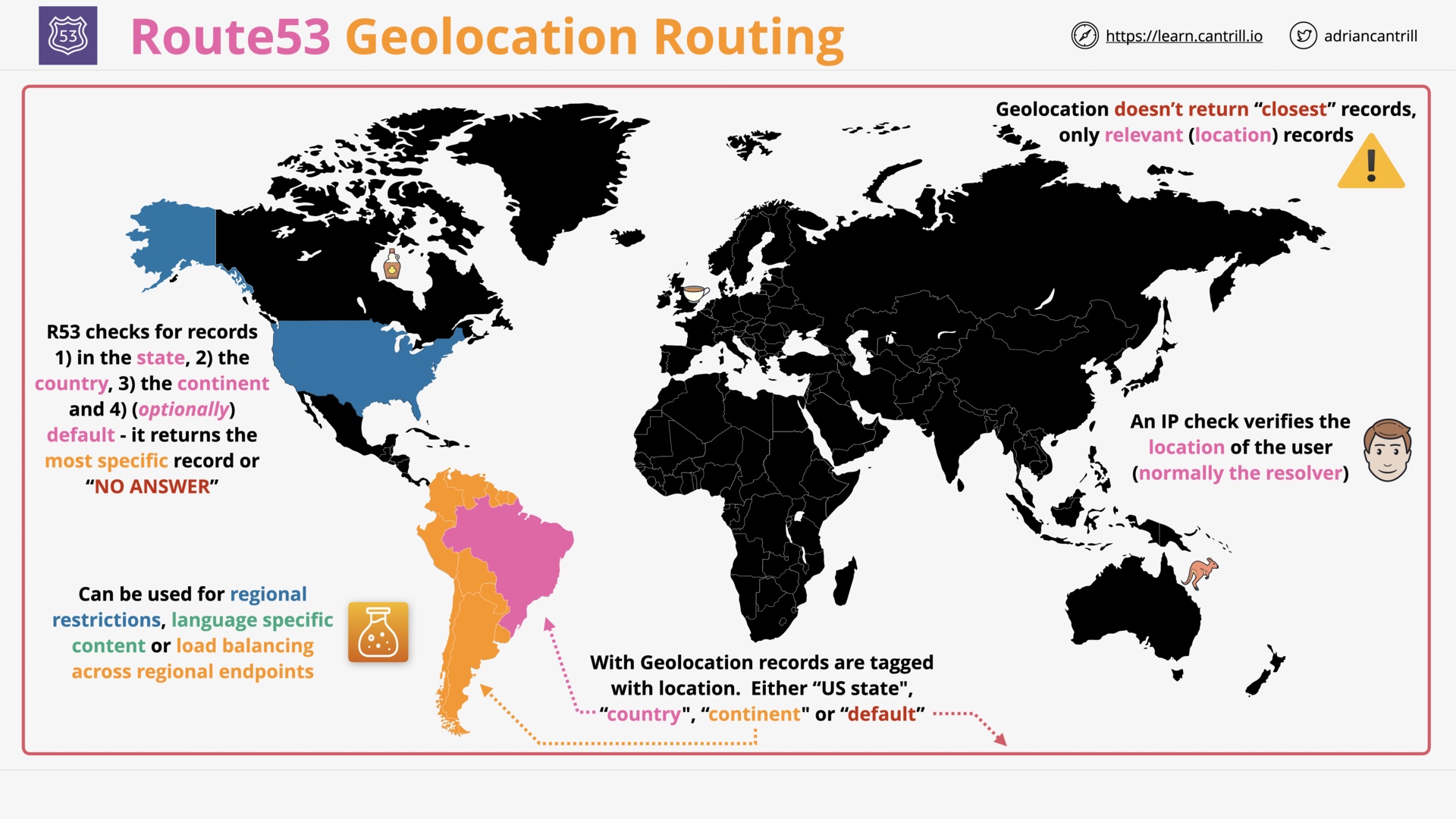
what is geolocation routing?
Routing traffic based on the geographic location of users:
- to localize content
- to restrict distribution of content
- …
Geoproximity Routing (4:50)
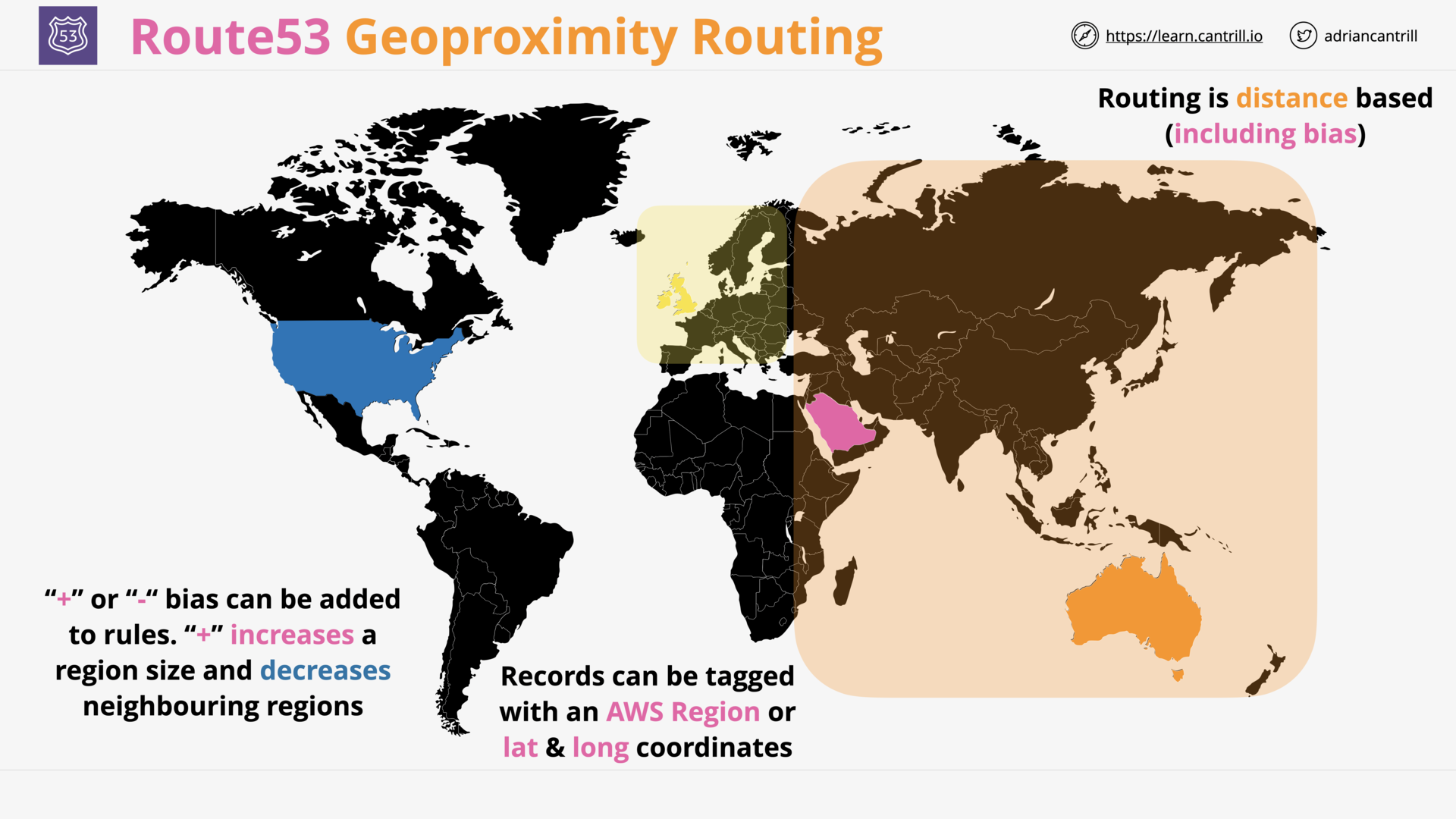
what is geoproximity routing?
Routing traffic based on the geographic location of users and our resources.
A ‘bias’ can be applied to expand/shrink the size of the geographic region.
compare `latency-based routing` - `geolocation routing` - `geoproximity routing`?
R53 Interoperability (11:50)
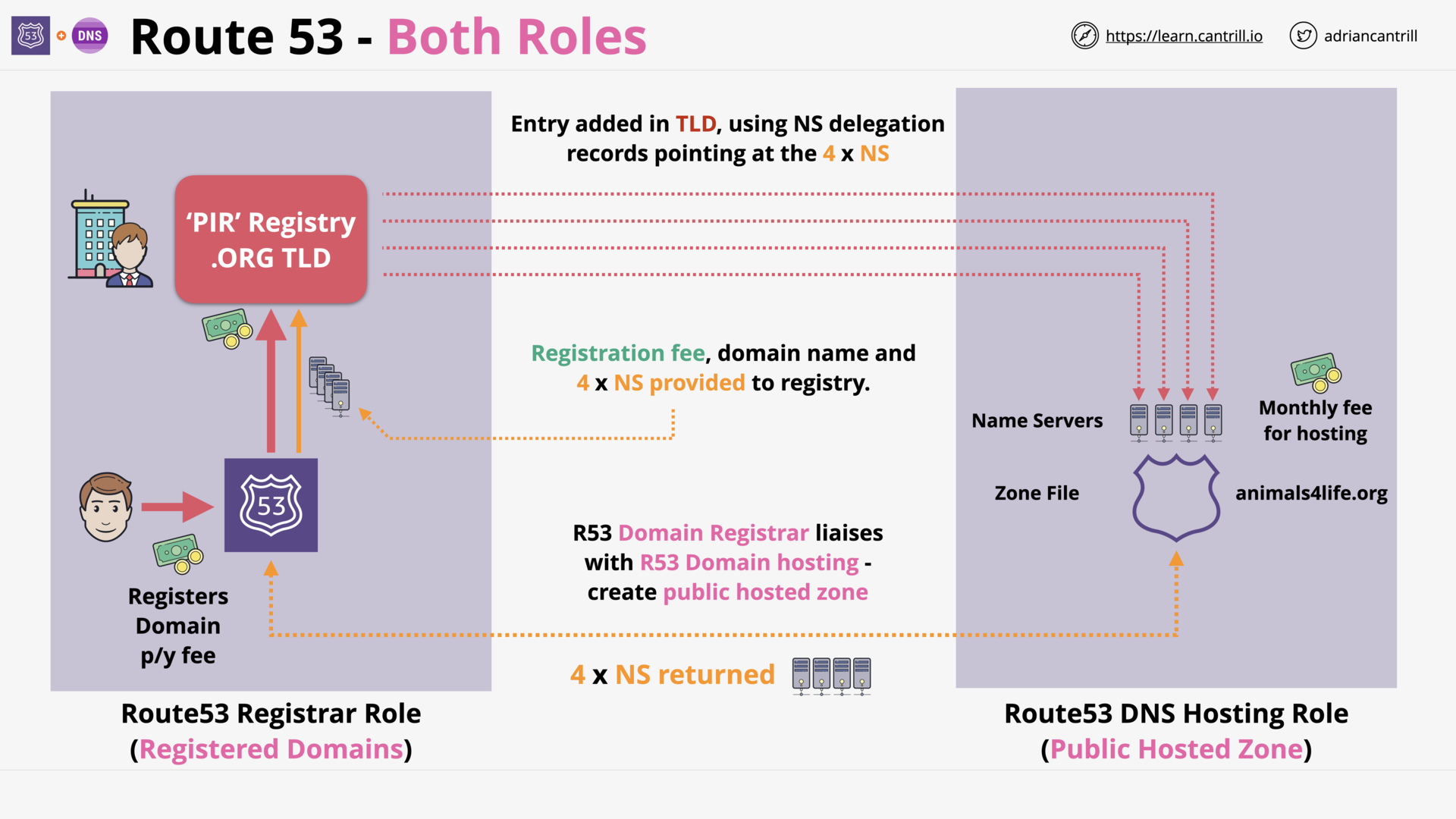 Route 53: Registrar + Hosting
Route 53: Registrar + Hosting
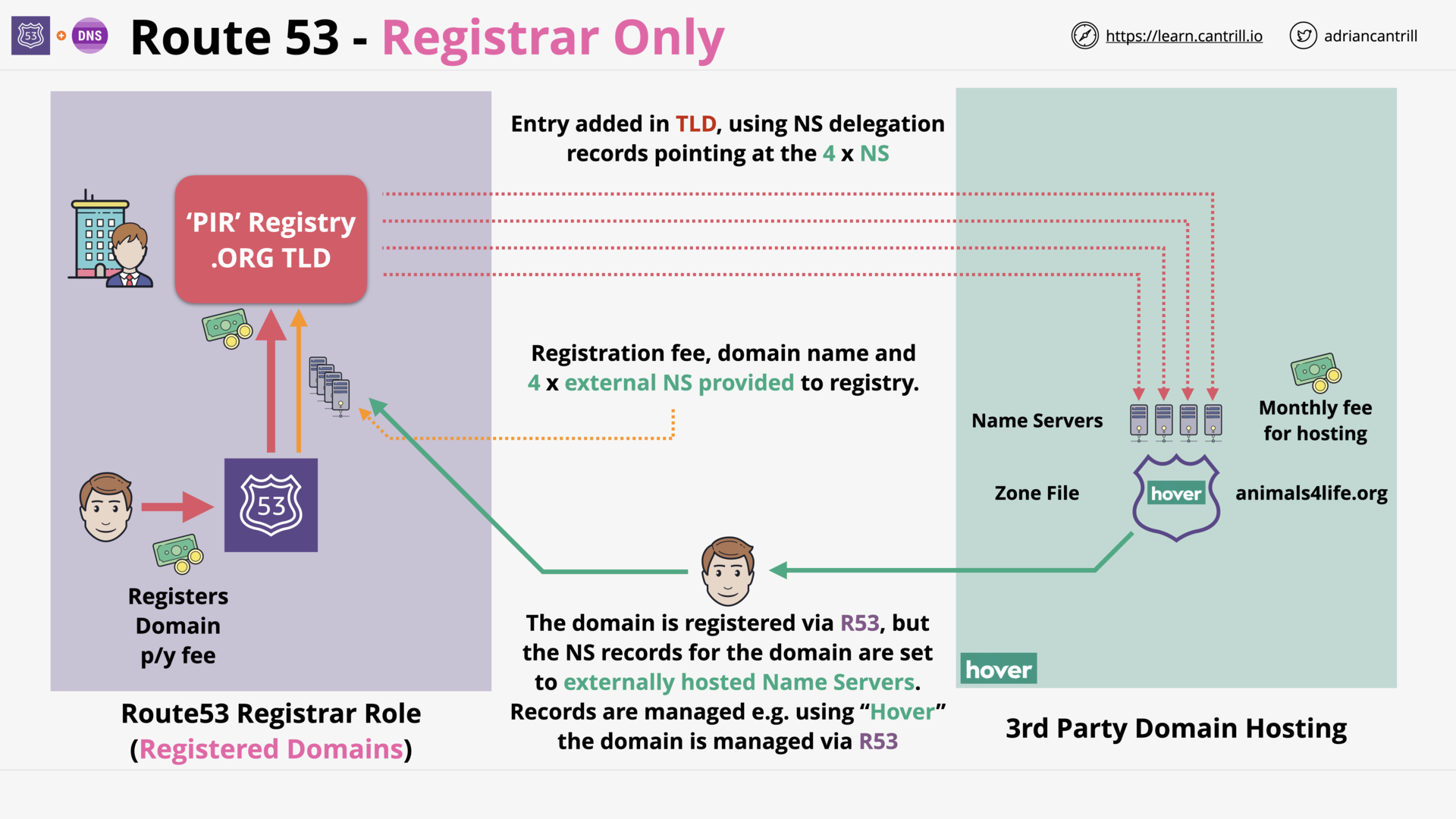 Route 53: Registrar Only
Route 53: Registrar Only
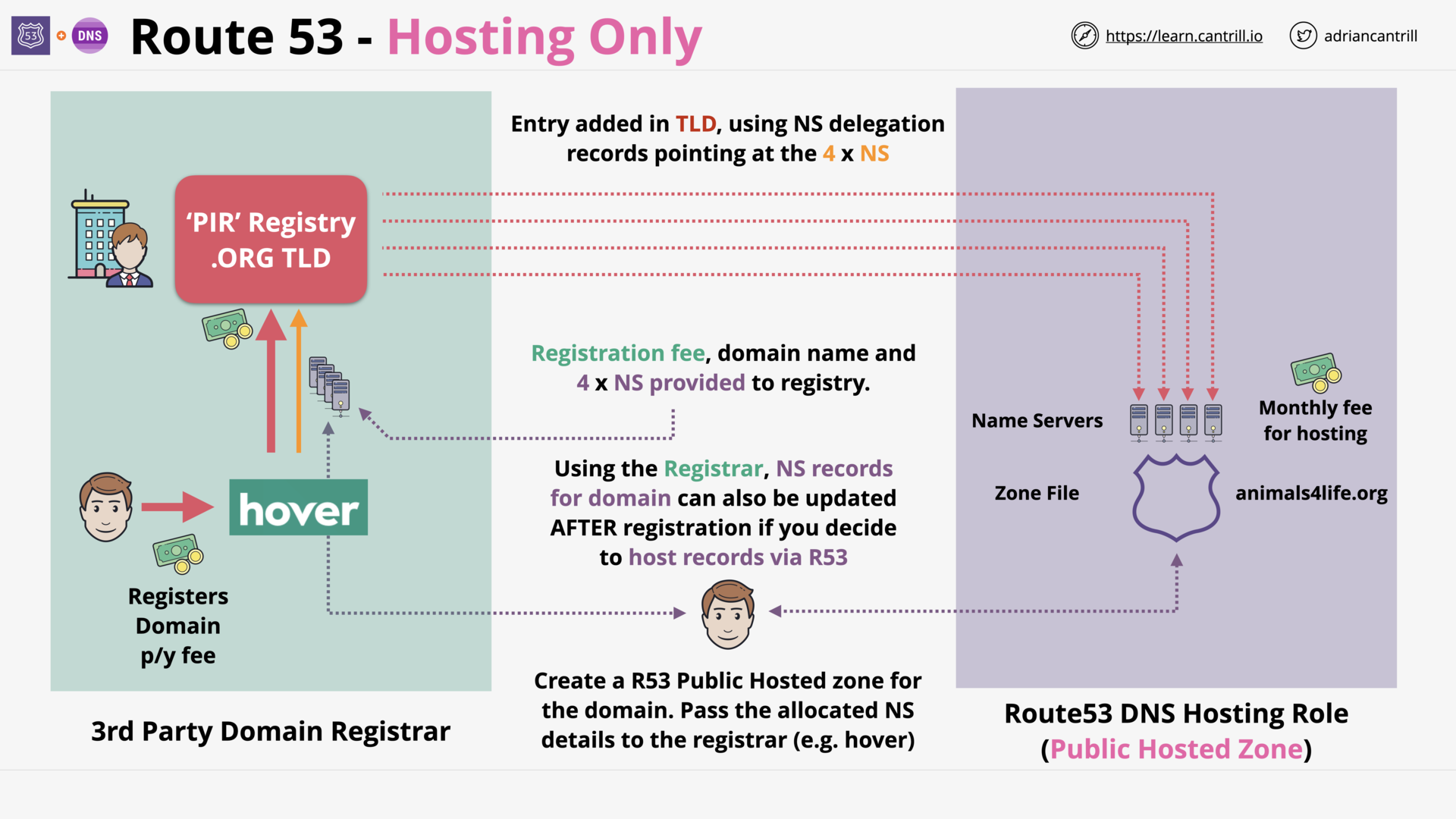 Route 53: Hosting Only
Route 53: Hosting Only