TUTORIALS DOJO - TIPS AND TRICKS
Analytics
Amazon Athena: Query data in Amazon S3 using SQL
athena vs redshift spectrum
SQL query data in S3
- Athena: Serverless, simple query
- Redshift Spectrum: Provision resources, complex query
Amazon EMR: Hosted Hadoop framework
csv store in s3, automated convert to parquet -> store in a s3 bucket; min operation cost
- Working Solutions:
- AWS Batch + bash script
- Amazon EMR
amazon emr: hosted hadoop framework
- Amazon EMR Serverless
AWS Glue: Simple, scalable, and serverless data integration
aws glue
- Serverless ETL
- Glue Job can be triggered manually or via events using EventBridge
aws glue - job bookmarking
- maintain state information and prevent the reprocessing of old data.
Amazon Kinesis: Analyze real-time video and data streams
- kinesis video streams: capture, process, and store video streams for analytics and machine learning.
- Kinesis Data Streams: Build custom applications that analyze data streams using popular stream-processing frameworks.
- Kinesis Data Firehose: Load data streams into AWS data stores.
kinesis data streams vs sqs
- Kinesis Data Streams: Provide real-time analyzing, but required provisioning shards
- SQS: Use with Lambda (and its Event Sourcing) provides a cost-efficient solution
asynchronous process, cost-effective (alternative to kinesis data streams)
SQS + Lambda
AWS Lake Formation: Build a secure data lake in days
Amazon QuickSight: Fast business analytics service
Amazon Redshift: Fast, simple, cost-effective data warehouse service
amazon redshift backup:
- Manually Snapshots
- Automatically increment backup:
- Every 8 hours or 5 GB of data
- 1-day retention (default, configurable up to 35 days)
Backup to S3 bucket, configurable to copy snapshots to another region for DR.
latency: redshift vs dynamodb
- Redshift: sub-second (s)
- DynamoDB: millisecond (ms)
redshift spectrum vs athena
SQL query data in S3
- Redshift Spectrum: Provision resources, complex query
- Athena: Serverless, simple query
Application Integration
Amazon EventBridge: Serverless event bus for SaaS apps and AWS services
Amazon MQ: Managed message broker service
amazon mq:
- A single-instance broker: is comprised of one broker in one Availability Zone behind a Network Load Balancer (NLB) The broker communicates with your application and with an Amazon EBS storage volume.
- A cluster deployment: is a logical grouping of three RabbitMQ broker nodes behind a Network Load Balancer, each sharing users, queues, and a distributed state across multiple Availability Zones (AZ).
Amazon SNS: Pub/sub, SMS, email, and mobile push notifications
Amazon SQS: Managed message queues
AWS Step Functions: Coordination for distributed applications
Amazon SWF: Build applications that coordinate work across distributed components
ensure a queue's messages are not process twice:
- SQS FIFO Queue
- Amazon Simple Workflow Service (Amazon SWF)
Business Applications
Amazon SES: High-scale inbound and outbound email
Amazon Pinpoint: Multichannel marketing communications |
Engage your customers by sending them email, SMS and voice messages, and push notifications.
- send targeted messages (such as promotions and retention campaigns)
- send transactional messages (such as order confirmations and password reset messages)
Cloud Financial Management
AWS Billing and Cost Management: Find features that help you pay your bills and optimize your costs
aws budgets: set custom budgets and receive alerts
aws cost explorer: visualize and explore your aws costs and usage
Compute
AWS Batch: Run batch jobs at any scale
csv store in s3, automated convert to parquet -> store in a s3 bucket; min operation cost
- Working Solutions:
- AWS Batch + bash script
- Amazon EMR
amazon emr: hosted hadoop framework
- Amazon EMR Serverless
Amazon EC2: Create and run virtual servers in the cloud
ec2 - hibernation
- Quickly pausing and resuming the instances, by saving the memory footprint to disk.
- Can only be enable at launch
- Pay as stopped instances:
- No hourly charging
- EBS volume.
- Elastic IP Address.
ec2 states:
- pending
- running 💸
- rebooting
- stopping - stopped (EBS-backed instances)
- hibernate 💸
- shutting-down
- terminated (Terminated Reserver Instances are still billed 💸)
ec2 - reserved instance
Reserved Instance Marketplace: Resell unused Standard Reserved Instances
ec2 - stop instance vs terminate instance
- Stopped: still be billed
- Terminated: not billed
ec2 - instance store:
- Its data will be lost if the EC2 instance is stopped / terminated.
ec2 - elastic ip address and ebs storage won't be effect after an instance is stopped.
security group referencing
When you specify a security group as the source or destination for a rule (of a security group), the rule affects all instances that are associated with the security groups.
eni - ena - efa
-
Elastic Network Interface (ENI): logical networking component in a VPC that represents a virtual network card
-
Elastic Network Adapter (ENA): High Performance Network Interface for Amazon EC2
- Enhanced networking: up to 100 Gbps
- provide traditional IP networking features
-
Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA): network device to accelerate High Performance Computing (HPC) applications
- support OS-bypass capabilities: allow HPC communicate directly with the EFA device.
fault tolerance: ability of a system to remain in operation even if some of the components used to build the system fail
cloudwatch alarm can stop, terminate, reboot, recover an ec2 instance
monitor ec2:
-
CloudWatch default metric
- CPU utilization from hypervisor
- Disk
- Network
-
CloudWatch Agent:
- Memory
- Sub-resource metrics such as per-CPU core
notify for ec2 instance:
-
All EC2 instances:
- Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule to check for AWS Personal Health Dashboard events that are related to Amazon EC2 instances.
- To send notifications, set an Amazon SNS topic as a target for the rule.
-
A specific EC2 instance:
Use CloudWatch Alarm and EC2 Action to interact with EC2 instance.
best practice to control access to ec2 instances:
- Tag the EC2 instances, to categorize by purpose, owner, or environment…
- Control access using resource tags and IAM policy.
ec2 - capacity reservations vs reserved instances
-
(On-demand) Capacity Reservations:
- Reserve compute capacity for your Amazon EC2 instances in a specific Availability Zone for any duration
- Full price
-
Reserve Instances:
- Regional Reserve Instances: Save money
- Zone Reserve Instances: Save money
ec2 - placement group - error adding instance 'insufficient capacity error'
- Amazon does not currently have enough available On-Demand capacity on the existing host to fulfill your request.
Workaround: Stop all instances, then start -> Maybe a new host have enough capacity
ec2 auto scaling group's [termination policy](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/as-instance-termination.html#default-termination-policy)
- Maximum availability: Kill instance in the AZs with the most instances (and oldest Launch Configuration)
- Keep most updated instance: Kill instance with oldest LC
- Maximum instance usage: Kill the instance closest to billing hour.
- Finally: random.
auto scaling group (asg) policies:
- Manually
- Scheduled
- Dynamic
- Simple
- Stepped
- Target Tracking
- Predictive
[data transfer]
- Data transferred between EC2 & RDS, Redshift, ElastiCache instances, and ENI in the same AZ is free.
- Data transferred directly between EC2 & S3, EBS direct APIs, Glacier, DynamoDB, SES, SQS, Kinesis, ECR, SNS or SimpleDB in the same AWS Region is free.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Run and manage web apps
Reduces the operational overhead by taking care of provisioning the needed resources for your application.
elastic beanstalk: run and manage web apps
-
Reduces the operational overhead by taking care of provisioning the needed resources for your application
-
Elastic Beanstalk supports:
- applications developed in Go, Java, .NET, Node.js, PHP, Python, and Ruby
- custom environment with Docker
-
When you deploy your application, Elastic Beanstalk
- builds the selected supported platform version
- provisions one or more AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances, to run your application.
elastic beanstalk vs ecs
-
Elastic Beanstalk:
Automatically handles the details of capacity provisioning, load balancing, scaling, and application health monitoring.
=> Quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without having to learn about the infrastructure that runs those applications
-
ECS:
Need to manually config Service Auto Scaling, Service Load Balancing, and Monitoring with CloudWatch
AWS Lambda: Run code without thinking about servers
allow an lambda permission to use kms:
- Attach the kms:decrypt permission to the Lambda function’s
execution role - Add a statement to the AWS KMS
key policythat grants the function’s execution role the kms:decrypt permission.
permission to invoke a lambda function
Use the Lambda function’s resource policy:
- Principal: the ARN of dev account
- Action: lambda:InvokeFunction
lambda function's `execution role`
Give the Lambda function permissions to access AWS resources.
AWS Wavelength: Deliver ultra-low latency applications for 5G devices
- Application traffic can reach application servers running in Wavelength Zones without leaving the mobile providers’ network
Containers
Amazon ECR: Easily store, manage, and deploy container images
Amazon ECS: Highly secure, reliable, and scalable way to run containers
elastic beanstalk vs ecs
-
Elastic Beanstalk:
Automatically handles the details of capacity provisioning, load balancing, scaling, and application health monitoring.
=> Quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without having to learn about the infrastructure that runs those applications
-
ECS:
Need to manually config Service Auto Scaling, Service Load Balancing, and Monitoring with CloudWatch
ecs auto scaling - metric:
-
ECS Instances (~ K8s Node):
- CPU Utilization
- Disk
- Disk Reads
- Disk Read Operations
- Disk Writes
- Disk Write Operations
- Network
- Network In
- Network Out
- Status Check Failed
- Status Check Failed (Any)
- Status Check Failed (Instance)
- Status Check Failed (System)
-
ECS Service (~ K8s Pod):
- ECSServiceAverageCPUUtilization
- ECSServiceAverageMemoryUtilization
- ALBRequestCountPerTarget
Amazon EKS: Run Kubernetes on AWS without operating your own Kubernetes clusters
iam and k8s:
- Enable with AWS IAM Authenticator for Kubernetes, which runs on the Amazon EKS control plane.
- The authenticator gets its configuration information from the aws-auth ConfigMap (AWS authenticator configuration map).
Cryptography & PKI
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM): Provision, manage, and deploy SSL/TLS certificates
which services support storing ssl certificate?
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- IAM SSL certificate storage (Used for region that not support ACM)
when using regional api gateway, the certificate for the domain name needs to be in the same region.
monitor expiration of certificates
- Option 1: Use the ACM built-in Certificate Expiration event
- ACM sends daily expiration events for all active certificates (public, private and imported) starting 45 days prior to expiration.
- AWS Health events are generated for ACM certificates that are eligible for renewal.
- Option 2: Use the
DaysToExpirymetric
AWS CloudHSM: Hardware-based key storage for regulatory compliance
AWS KMS: Managed creation and control of encryption keys
k8s has its own mechanism for storing secret, which are default store as plain text in etcd key-value store.
We can apply envelope encryption to encrypt these secrets with AWS KMS before stored them in etcd store.
kms - [custom key store](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/custom-key-store-overview.html)
-> We own and manage
allow an lambda permission to use kms:
- Attach the kms:decrypt permission to the Lambda function’s
execution role - Add a statement to the AWS KMS
key policythat grants the function’s execution role the kms:decrypt permission.
s3 object encryption:
-
Server-Side Encryption (SSE):
- SSE-S3 (Amazon S3 managed keys)
- SSE-KMS (AWS KMS)
- SSE-C (Customer-provided keys)
-
Client-Side Encryption (CSE):
- CSE-KMS-CMK
- CSE-Client Master key
| Encryption | Fullname | Who Manages Key? | Who Manages Encryption Process? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSE-S3 | SSE with Amazon S3 managed keys | S3 | S3 | Default |
| SSE-KMS | SSE with AWS KMS keys | AWS managed key | S3 | Support audit keys usage… |
| Customer managed key (CMK) - Renamed to KMS Key | ||||
| SSE-C | SSE with Customer-Provided Key | Customer | S3 | Use your own encryption key |
| CSE | Customer | Customer |
Database
Amazon Aurora: High performance managed relational database engine
aurora auto scaling vs aurora serverless
- Aurora Auto Scaling: Dynamically adjusts the number of Aurora Replicas (reader DB instances) provisioned for an Aurora DB cluster.
- Aurora Serverless: On-demand, autoscaling the capacity of Aurora DB cluster resource
aurora serverless
- The DB instance cannot be changed from Provisioned to Serverless after created.
- After the DB instanced is created, need to use AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) to migrate data from the existing DB cluster to a new Aurora Serverless database.
aurora custom endpoint: provides load-balanced database connections based on criteria other than the read-only or read-write capability of the db instances
aurora - reader endpoint:
- A reader endpoint for an Aurora DB cluster provides load-balancing support for read-only connections to the DB cluster
aurora failover: automatically handled by amazon aurora
-
If you have an Amazon Aurora Replica
Amazon Aurora flips the canonical name record (CNAME) for your DB Instance to point at the healthy replica
-
If you are running Aurora Serverless and the DB instance or AZ becomes unavailable
Aurora will automatically recreate the DB instance in a different AZ.
-
Otherwise:
Aurora will attempt to create a new DB Instance in the same Availability Zone as the original instance.
The replacement is done on a best-effort basis and may not succeed
aurora - clone:
- Creating a Aurora clone is faster and more space-efficient than physically copying the data using other techniques, such as restoring from a snapshot like you would in Amazon RDS
- Aurora uses a copy-on-write protocol to create a clone.
aurora - storage:
- Aurora data is stored in the cluster volume, which is a single, virtual volume that uses solid state drives (SSDs)
- A cluster volume consists of copies of the data across three Availability Zones in a single AWS Region.
- The data is automatically replicated across Availability Zones,
- A cluster volume consists of copies of the data across three Availability Zones in a single AWS Region.
Amazon DynamoDB: Managed NoSQL database
latency: redshift vs dynamodb
- Redshift: sub-second (s)
- DynamoDB: millisecond (ms)
Amazon ElastiCache: In-memory caching service
elasticache - redis vs memcached
- Redis: Advance structure, replicas
- Memcached: Multi-threads, multi-nodes.
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database - QLDB: Fully managed ledger database
Provides a transparent, immutable, and cryptographically verifiable transaction log owned by a central trusted authority.
👉 Track all application data changes, and maintain a complete and verifiable history of changes over time.
Amazon RDS: Set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud
rds enhanced monitoring
- CloudWatch gathers metrics about CPU utilization from the hypervisor for a DB instance
- Enhanced Monitoring gathers its metrics from an agent on the instance ~ EC2 CloudWatch Agent
monitor rds:
-
Default metric
- CPU utilization from hypervisor
- Database connections
- Free memory
-
Enhanced Monitoring:
- OS processes
- RDS processes
rds - [iam db authentication](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazonrds/latest/userguide/usingwithrds.iamdbauth.html)
To connect to DB instance, we’ll use an authentication token (generated using the IAM role’s credential).
rds - “too many connections”
RDS Proxy: allow your applications to pool and share database connections to improve their ability to scale.
rds multi-az failover:
-
Loss of availability in primary Availability Zone
-
Primary DB instance:
- Loss of network connectivity to primary
- Compute unit failure on primary
- Storage failure on primary
-
DB instance scaling or system upgrades:
Applied first on the standby prior then automatic failover
use secure sockets layer (ssl) to encrypt connections between your client applications and your amazon rds db instances running microsoft sql server.
- Download the Amazon RDS Root CA certificate. Import the certificate to your servers and configure your application to use SSL to encrypt the connection to RDS.
- Force all connections to your DB instance to use SSL by setting the rds.force_ssl parameter to true. Once done, reboot your DB instance.
Front-End Web & Mobile
AWS AppSync: Accelerate app development with fully-managed, scalable GraphQL APIs
aws appsync pipeline resolver: orchestrating requests to multiple data sources.
Simplify client-side application complexity and help enforce server-side business logic controls by
Machine Learning
Amazon Comprehend: Discover insights and relationships in text
Amazon Comprehend Medical: Detect and return useful information in unstructured clinical text
AWS Deep Learning AMI: Deep learning on Amazon EC2
Amazon Forecast: Increase forecast accuracy using machine learning
Amazon Fraud Detector: Detect more online fraud faster
Amazon Kendra: Reinvent enterprise search with ML
Amazon Lex: Build voice and text chatbots
Amazon Polly: Turn text into life-like speech
Amazon Rekognition: Analyze image and video
Amazon SageMaker: Build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale
Amazon Textract: Extract text and data from documents
Amazon Transcribe: Automatic speech recognition
Amazon Translate: Natural and fluent language translation
Management & Governance
Auto Scaling: Scale multiple resources to meet demand
AWS CloudFormation: Create and manage resources with templates
cloudformation: creationpolicy & cfn-signal
- CreationPolicy: Wait on resource configuration actions before stack creation proceeds.
- cfn-signal: Signals CloudFormation to indicate whether Amazon EC2 instances have been successfully created/updated
AWS CloudTrail: Track and monitor activities by users, roles, or AWS services
cloudtrail - encryption
By default, CloudTrail event log files are encrypted using Amazon S3 server-side encryption (SSE)
cloudtrail logs vs s3 server access logs
- CloudTrail Logs: record of actions taken by a user, role, or an AWS service in Amazon S3
- S3 server access logs: detailed records for the requests that are made to an S3 bucket
- Fields for Object Size, Total Time, Turn-Around Time, and HTTP Referrer for log records
- Lifecycle transitions, expirations, restores
- Invalid Authentication
Amazon CloudWatch: Monitor resources and applications
cloudwatch alarm can stop, terminate, reboot, recover an ec2 instance
monitor ec2:
-
CloudWatch default metric
- CPU utilization from hypervisor
- Disk
- Network
-
CloudWatch Agent:
- Memory
- Sub-resource metrics such as per-CPU core
monitor rds:
-
Default metric
- CPU utilization from hypervisor
- Database connections
- Free memory
-
Enhanced Monitoring:
- OS processes
- RDS processes
monitor expiration of certificates
- Option 1: Use the ACM built-in Certificate Expiration event
- ACM sends daily expiration events for all active certificates (public, private and imported) starting 45 days prior to expiration.
- AWS Health events are generated for ACM certificates that are eligible for renewal.
- Option 2: Use the
DaysToExpirymetric
AWS CLI: Command line interface tool to manage AWS services
AWS Compute Optimizer: Identify optimal AWS compute resources |
- analyzes the configuration and utilization metrics of your aws resources
- Reports whether your resources are optimal
- Generates optimization recommendations to reduce the cost and improve the performance of your workloads
AWS Config: Track and evaluate configuration changes
AWS Control Tower: Set up and govern a secure, compliant multi-account environment
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager: Automate management of Amazon EBS snapshots and Amazon EBS-backed AMIs
AWS Health: Find information about events that can affect your AWS resources
AWS License Manager: Track and manage software licenses across multiple AWS Regions
Amazon Managed Grafana: Visualize and analyze your operational data at scale
Visualize metrics to dashboard
Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus: Highly available, secure, and managed monitoring for your containers
Collects metrics
AWS Management Console: Web-based user interface comprising multiple AWS service consoles
AWS Organizations: Central governance and management across AWS accounts
service control policy (scp): a feature of aws organizations
- A type of organization policy that you can use to manage permissions in your organization.
AWS Proton: Automate management for container and serverless deployments
AWS Systems Manager: Gain operational insights and take action
aws systems manager's fleet manager: ui for managing nodes/ec2 instance.
Tag Editor: Add, edit, or delete tags on multiple AWS resources
AWS Trusted Advisor: Optimize performance and security
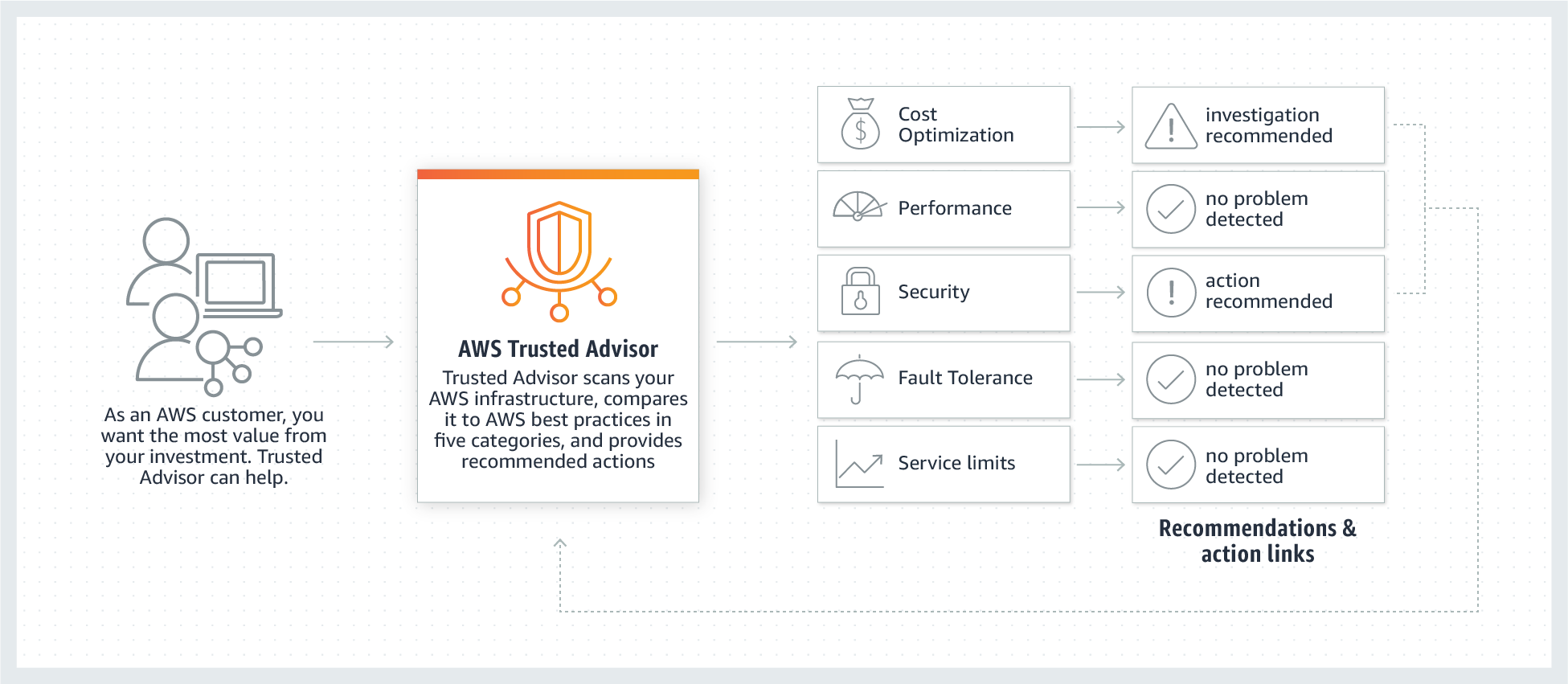
Inspects your AWS environment and recommends ways to save money, close security gaps, and improve system availability and performance.
**aws trusted advisor** _service limits_:
- Monitor the service quotas in all Regions.
- Alerts you if your account reaches more than 80% of a service quota in any Region.
AWS Well-Architected Tool: Review and improve your workloads
CloudWatch
cloudwatch - cloudwatch logs - cloudtrail - cloudwatch events - eventbridge?
-
CloudWatch: Monitor resources and applications
Monitor your AWS resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time.
- CloudWatch Logs: Monitor, store, and access your log files from Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud instances, AWS CloudTrail, or other sources.
- CloudWatch Logs Insights: query logs with SQL-like syntax
- CLoudWatch Events: Is now Amazon EventBridge
CloudTrail
- cloudtrail: track and monitor activities by users, roles, or aws services
Migration & Transfer
AWS Application Discovery Service: Discover on-premises applications to streamline migration
AWS Application Migration Service: Automate application migration and modernization
AWS Database Migration Service: Migrate databases with minimal downtime
Migrate on-premises databases to the AWS Cloud.
replicate database on s3 as csv, stream on-going changes, min management overhead
AWS Database Migration Service + Change Data Capture (CDC)
AWS DataSync: Simple, fast, online data transfer
An online data movement and discovery service that simplifies data migration and helps you quickly, easily, and securely transfer your file or object data to, from, and between AWS storage services.
AWS Schema Conversion Tool: Convert source schema and most code to target-compatible format
Networking & Content Delivery
Amazon API Gateway: Build, deploy, and manage APIs
api gateway works at any scale, just pay money.
Throttle API requests for our budget (and for better throughtput)
when using regional api gateway, the certificate for the domain name needs to be in the same region.
Amazon CloudFront: Global content delivery network
cloudfront supports `geo blocking` (`geographic restrictions`)
lambda@edge: run lambda functions to customize the content that cloudfront delivers
cloudfront - origin _failover_
Needs an origin groups with 2 origin:
- a primary origin
- a secondary origin
cloudfront cannot host data, only cache data.
AWS Direct Connect: Dedicated network connection to AWS
from your on-premises network
Elastic Load Balancing: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple targets
elastic load balancer protocol:
- Application Load Balancer: HTTP/s and gRPC
- Network Load Balancer: TCP, UDP, TLS
- Gateway Load Balancer: IP
application load balancer: supports weighted target groups
nlb: only support tcp, udp, tls, but it can perform http/s health check.
elb - access logs
Capture detailed information about requests sent to your load balancer
- Disabled by default
Ref:
aws services with access logs:
- S3
- ELB
- CloudFront: or standard logs
- API Gateway
AWS Global Accelerator: Improve global application availability and performance
Improve application availability, performance, and security using the AWS global network
What is it?
A service in which you create accelerators to improve the performance of your applications for local and global users
How it works?
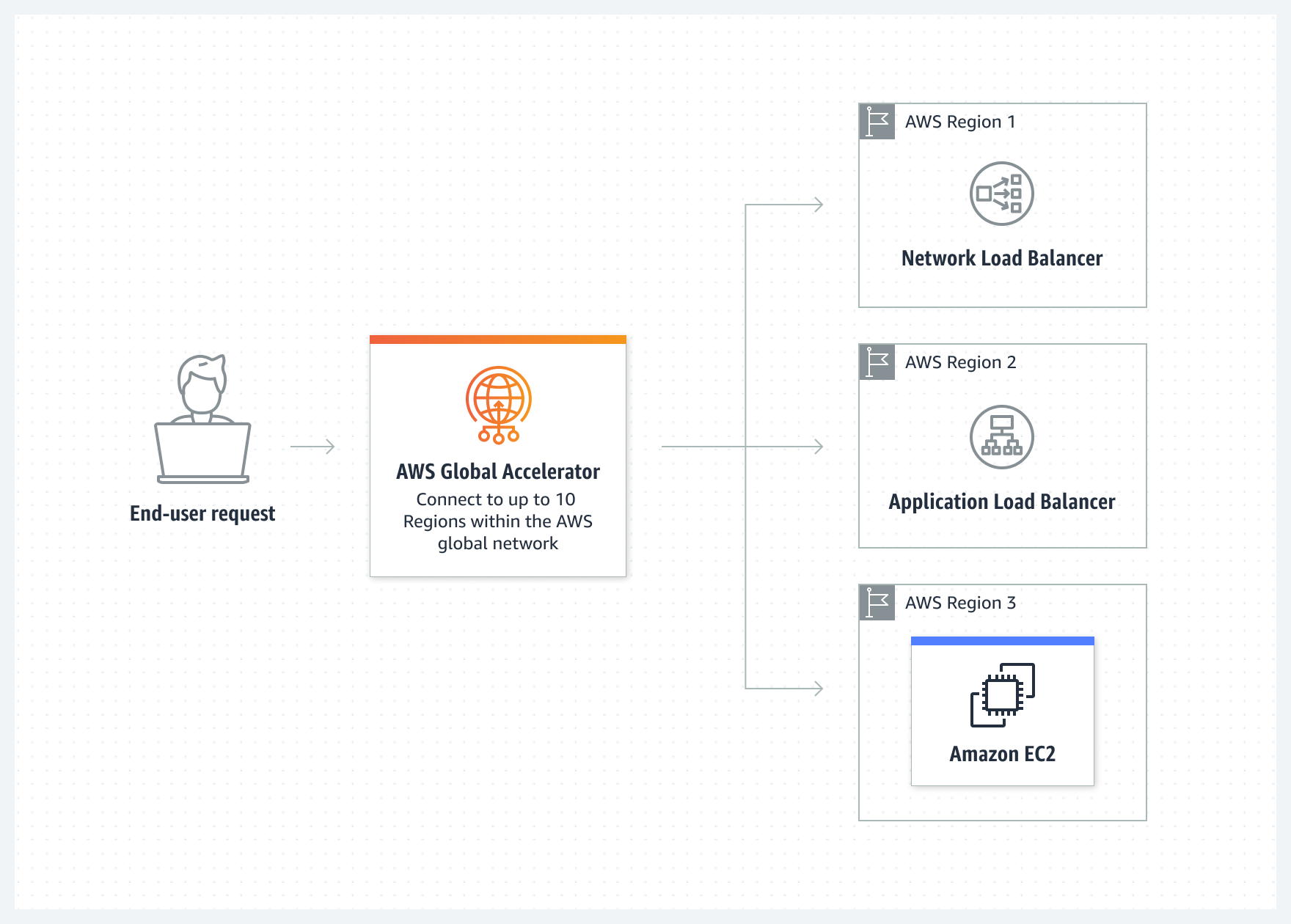
Why use it?
- Take advantage of AWS Global Infrastructure to onboard your user traffic at one of the Global Accelerator edge locations.
- Users can access your application endpoints through static IP addresses to enjoy deterministic routing independent of DNS.
Use cases
-
Global traffic manager Use traffic dials to route traffic to the nearest Region or achieve fast failover across Regions.
-
API acceleration Accelerate API workloads by up to 60%, leveraging TCP termination at the edge.
-
Global static IP Simplify allowlisting in enterprise firewalling and IoT use cases.
-
Low-latency gaming and media workloads Use custom routing to deterministically route traffic to a fleet of EC2 instances.
Related Services
global accelerator & elb
global accelerator vs cloudfront
Notes
Amazon Route 53: Highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service
route 53: geoproximity routing vs geolocation routing vs latency-based routing
- Geolocation Routing: Location of user
- GeoProximity Routing: Location of user AND AWS resources (with bias)
- Latency-based Routing
cname record vs route 53 alias record
- CNAME record: doesn’t work with zone apex (root domain name)
- Route 53 alias record:
- make CNAME record work with zone apex 👉 can create alias CNAME to point to another domain
- make other record point to domain name
- can point to AWS resources e.g. An alias A Record point to DNS name of a LB
Amazon VPC: Isolated cloud resources
data transfer
- S3: within the same Region is free.
- Others (EC2) within the same Availability Zone is free.
vpc peering: only works for vpcs, doesn't work with on-premise networks
vpc peering - setup
- Create, invite, accept VPC Peering Connection
- Update each VPC’s Route Table to point to IP range of other VPC.
vpc: ipv4 vs ipv6
- IPv4 is the default IP addressing system for VPC => Cannot be disabled
- IPv6: optional
vpc supports cidr blocks from /16 to /28
cidr `/0`: the entire network -> is not used in sg and nacl.
CIDR /32: One IP address.
vpc endpoints for s3: provide _private_ access to aws public services (s3)
-
Gateway endpoint:
- via Route Table’s Prefix List, without IGW, NATGW, PrivateLink
- Free
-
Interface endpoint:
-
via DNS using Private IP Address 👉 more features
- access from on-premises
- access from VPC in another AWS Region (using VPC Peering, Transit Gateway)
-
Billed 💸
-
vpc - nacl:
- The client that initiates the request chooses the ephemeral port range.
- In practice, to cover the different types of clients that might initiate traffic to public-facing instances in your VPC, you can open ephemeral ports 1024-65535.
To turn on the connection to a service running on an instance, the associated network ACL must allow the following:
- Inbound traffic on the port that the service is listening on
- Outbound traffic to ephemeral ports
eni - ena - efa
-
Elastic Network Interface (ENI): logical networking component in a VPC that represents a virtual network card
-
Elastic Network Adapter (ENA): High Performance Network Interface for Amazon EC2
- Enhanced networking: up to 100 Gbps
- provide traditional IP networking features
-
Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA): network device to accelerate High Performance Computing (HPC) applications
- support OS-bypass capabilities: allow HPC communicate directly with the EFA device.
security group referencing
When you specify a security group as the source or destination for a rule (of a security group), the rule affects all instances that are associated with the security groups.
default nacl allows all inbound and outbound traffic
s3 - restrict access to a vpc
👉 S3 Access Point
AWS VPN: Securely access your network resources
By establishing a secure and private tunnel from your network or device to the AWS Cloud.)
- aws site-to-site vpn: aws managed vpn services
- AWS Client VPN: client-based managed VPN service
aws site-to-site vpn throughput limit: 1.25 gbps
-
Scale VPN with Transit Gateway - Equal Cost Multipath Routing (ECMP).
Establish multiple VPN tunnels to an ECMP-enabled transit gateway
Security, Identity, & Compliance
AWS Artifact: On-demand access to AWS compliance reports
Reports
Amazon Cognito: Identity management for your apps
- Customer already has Active Directory Service -> No need to use Amazon Cognito -> use AWS IAM Identity Center with the Active Director Connector
AWS Directory Service: Set up and run Microsoft Active Directory with AWS services
AWS Firewall Manager: Deploy network security across your VPCs with just a few clicks
Simplifies your AWS WAF administration and maintenance tasks across multiple accounts and resources
Amazon GuardDuty: Managed threat detection service
Identify unexpected and potentially unauthorized or malicious activity in your AWS environment.
block sql injection
- AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF): can block SQL injection.
- GuardDuty: only detect SQL injection, not block.
AWS Identity and Access Management - IAM: Securely manage access to services and resources
authenticate for making api calls to aws resources
- Long-term credentials: Access key
[identity federation (with saml)](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/singlesignon/latest/userguide/samlfederationconcept.html): pass information about a user between
- a SAML authority (called an identity provider or IdP)
- a SAML consumer (called a service provider or SP)
iam identity provider (idp): manage user identities outside of aws and give these external user identities permissions to use aws resources in your account.
- Setup Identity Provider and Identity Federation.
- Setup an AWS Security Token Service to generate temporary tokens (STS supports SAML)
- Configure an IAM role and an IAM Policy to access the bucket.
iam group
- Cannot attach an IAM Role to an IAM Group.
which services support storing ssl certificate?
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- IAM SSL certificate storage (Used for region that not support ACM)
iam and eks:
- Enable with AWS IAM Authenticator for Kubernetes, which runs on the Amazon EKS control plane.
- The authenticator gets its configuration information from the aws-auth ConfigMap (AWS authenticator configuration map).
iam cross-account access: delegate access across aws accounts
e.g. 2 accounts for resources:
Productionaccount: For production resourcesDevelopmentaccount: For developments resources
IAM user groups: Developers can
- Always access resources in
Development - From time to time, access resources in
Productionaccount.
AWS IAM Identity Center: Manage single sign-on access to AWS accounts and apps
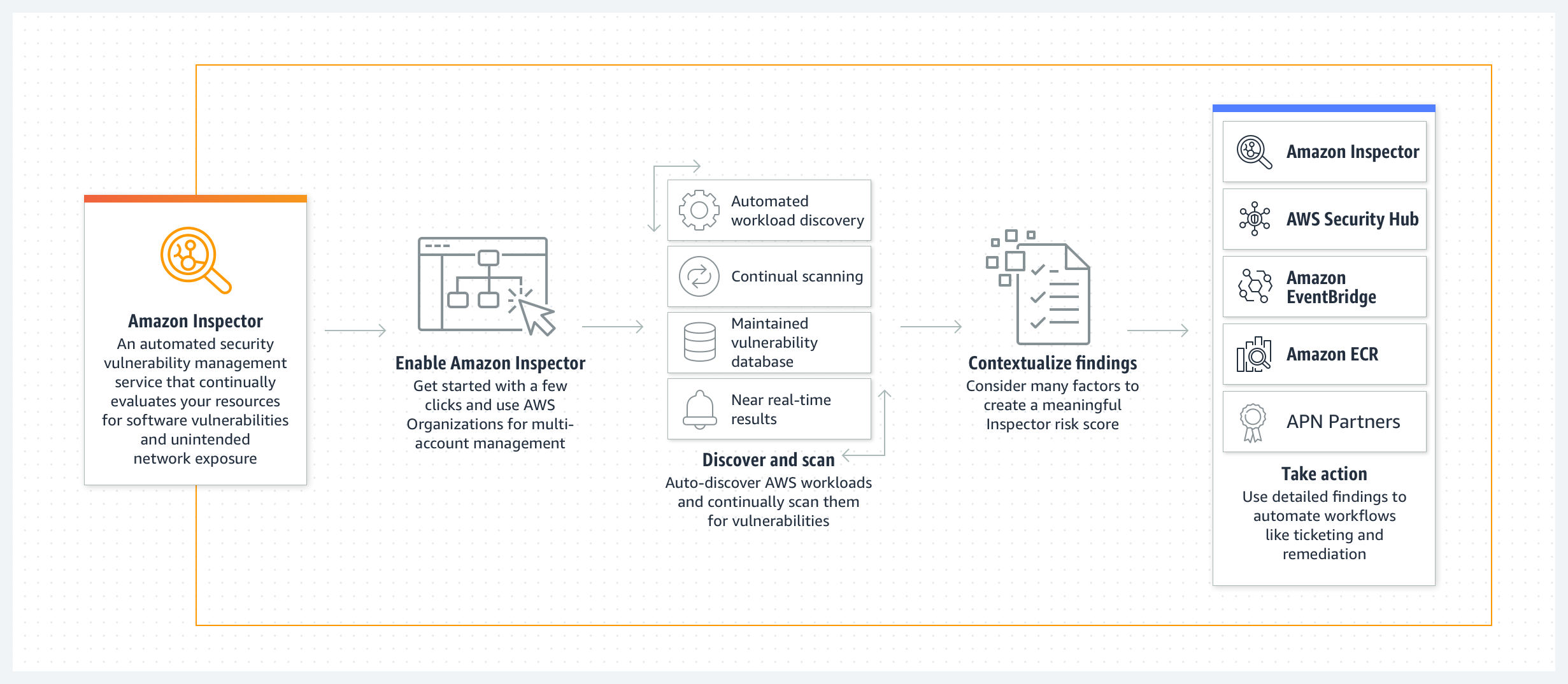
Amazon Inspector: Automated and continual vulnerability management at scale
EC2, ECR, Lambda
Amazon Macie: Discover and protect your sensitive data at scale
S3
AWS Network Firewall: Deploy network security across your Amazon VPCs with just a few clicks
A stateful, managed, network firewall and intrusion detection and prevention service for your virtual private cloud (VPC).
Traffic from VPC need to be routed to Network Firewall through the firewall endpoints.
AWS Resource Access Manager: Simple, secure service to share AWS resources
AWS Secrets Manager: Rotate, manage, and retrieve secrets
AWS Security Hub: Unified security and compliance center |
Dashboard / Overview
AWS Shield: DDoS protection
AWS WAF: Filter malicious web traffic
XSS, SQL-injection
[aws waf, aws shield, and aws firewall manager](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/waf/latest/developerguide/what-is-aws-waf.html): used together to create a comprehensive security solution
-
AWS WAF: Protect your web applications from common exploits
- Monitor web requests that your end users send to your applications and to control access to your content.
- Used for API Gateway, Load Balancer, Cloudfront.
- Block SQL injection, XSS (cross-site scripting)
- Can minimize the effects of a DDOS attack
-
AWS Shield: Managed DDoS protection
- Provides protection against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks for AWS resources, at the network and transport layers (layer 3 and 4) and the application layer (layer 7)
- Can use for more services: EC2, Route53
- Shield Standard: Free, L3-L4
- Shield Advanced: Cost money, L7
-
AWS Firewall Manager: Centrally configure and manage firewall rules across your accounts
Provides management of protections like AWS WAF and Shield Advanced across accounts and resources, even as new resources are added.
Serverless
Amazon API Gateway: Build, deploy, and manage APIs
AWS AppSync: Accelerate app development with fully-managed, scalable GraphQL APIs
Amazon DynamoDB: Managed NoSQL database
Amazon EventBridge: Serverless event bus for SaaS apps and AWS services
AWS Fargate: Serverless compute for containers
aws fargate: serverless compute for containers
By default, Fargate tasks are given a minimum of 20 GiB of free ephemeral storage
AWS Lambda: Run code without thinking about servers
Amazon S3: Object storage built to retrieve any amount of data from anywhere
Amazon SNS: Pub/sub, SMS, email, and mobile push notifications
AWS Step Functions: Coordinate components for distributed applications
Amazon SQS: Managed message queues
ensure a queue's messages are not process twice:
- SQS FIFO Queue
- Amazon Simple Workflow Service (Amazon SWF)
asynchronous process, cost-effective
SQS + Lambda
Storage
AWS Backup: Centralized backup across AWS services
Amazon EBS: Amazon EC2 block storage volumes
ebs is not suitable for archiving datasets -> s3 is better option
ebs - backup: use amazon data lifecycle manager (amazon dlm)
raid 0:
- I/O is distributed across the volumes in a stripe
- higher level of performance for a file system than you can provision on a single Amazon EBS volume
RAID 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6: NOT recommended for EBS
ebs encryption
- Data at rest inside the volume 👈 Encryption at rest
- All data moving between the volume and the instance 👈 Encryption in-transit
- All snapshots created from the volume
- All volumes created from those snapshots
Amazon EFS: Fully managed file system for Amazon EC2
efs vs storage gateway
- EFS: files are stored on AWS -> high-latency
- Storage Gateway - File: low-latency
Amazon FSx: Launch, run, and scale feature-rich and high-performing file systems
fsx
- FSx for Lustre: Linux, HPC
- FSx for Windows File Server
Amazon S3: Object storage built to retrieve any amount of data from anywhere
kms-managed cmk: key will be sent to aws
Server-side encryption: unencrypted data will be sent to AWS
-> Client-side encryption with a client-side master key.
s3 object lock
-
Retention:
-
Retention Mode:
- Governance: Big Brother can by pass it.
- Compliance: It’s universe law, nobody can do anything
-
Retention Period: A fixed period of time during which an object remains locked
-
-
Legal holds: ~ Retention Periods but has no expiration date
s3 static website - custom domain: "the s3 bucket name must be the same as the domain name"
What if someone use my domain name for their bucket ??? TODO
s3 - read data from glacier
- Bulk: Lowest (5-12 hours), cheapest
- Standard: 3-5 hours
- Expedited: Fastest (1-5 mins)
- Buy Provisioned capacity to ensure Expedited retrievals is available.
s3 object encryption:
-
Server-Side Encryption (SSE):
- SSE-S3 (Amazon S3 managed keys)
- SSE-KMS (AWS KMS)
- SSE-C (Customer-provided keys)
-
Client-Side Encryption (CSE):
- CSE-KMS-CMK
- CSE-Client Master key
by default, all amazon s3 resources such as buckets, objects, and related subresources are private.
To public all objects in a bucket:
- Unblocking the bucket. -> Configure the S3 bucket policy to set all objects to public read.
- Explicit allows public read -> Using bucket policy.
- Or manually public objects -> Grant public read access to the object when uploading it using the S3 Console.
vpc endpoints for s3: provide _private_ access to aws public services (s3)
-
Gateway endpoint:
- via Route Table’s Prefix List, without IGW, NATGW, PrivateLink
- Free
-
Interface endpoint:
-
via DNS using Private IP Address 👉 more features
- access from on-premises
- access from VPC in another AWS Region (using VPC Peering, Transit Gateway)
-
Billed 💸
-
s3 select: filter objects with sql syntax using bucket name & object key
s3 - requester pay
- In general, bucket owners pay for all Amazon S3 storage and data transfer costs that are associated with their bucket.
- With Requester Pays buckets,
- The requester (instead of the bucket owner) pays the cost of the request and the data download from the bucket.
- The bucket owner always pays the cost of storing data.
s3 - pii:
- Use Amazon Macie to automatically detect sensitive data.
- Then use EventBridge and SNS to send notification.
s3 - min storage duration
| Storage Class | Min Storage Duration |
|---|---|
| Standard, Intelligent-Tier | - |
| Standard-IA, One Zone - IA | 30 days |
| Glacier Instant/Flexible Retrieval | 90 days |
| Glacier Deep Archive | 180 days |
s3 standard-ia or s3 one zone-ia:
- Minimum Days for Transition from Standard: 30 days
- Minimum 30-Day Storage Charge: 30 days
data transfer
- S3: within the same Region is free.
- Others (EC2) within the same Availability Zone is free.
replicate database on s3 as csv, stream on-going changes, min management overhead
AWS Database Migration Service + Change Data Capture (CDC)
s3 - worm
👉 S3 - Object Lock + Legal Hold
s3 - restrict access to a vpc
👉 S3 Access Point
s3 server access logs vs cloudtrail logs
- CloudTrail Logs: record of actions taken by a user, role, or an AWS service in Amazon S3
- S3 server access logs: detailed records for the requests that are made to an S3 bucket
- Fields for Object Size, Total Time, Turn-Around Time, and HTTP Referrer for log records
- Lifecycle transitions, expirations, restores
- Invalid Authentication
aws services with access logs:
- S3
- ELB
- CloudFront: or standard logs
- API Gateway
Amazon S3 Glacier: Low-cost archive storage in the AWS Cloud
amazon glacier select: ffilter objects with sql syntax using bucket name & object key
AWS Snow Family: Move petabytes of data to and from AWS, or process data at the edge
aws snow family:
- Snowcone: 8TB - 14TB
- Snowball: 80TB
- Snowball Edge:
- Snowball Edge Compute Optimized: 80TB + EC2
- Snowball Edge Storage Optimized: 210TB + EC2
- Snowmobile: 100PB
aws opshub: graphical user interface to manage aws snowball devices
AWS Storage Gateway: Hybrid storage integration
nfs vs storage gateway
- NFS: files are stored on AWS -> high-latency
- Storage Gateway - File: low-latency
aws file gateway - handle writes
-
When a client writes data to a file via File Gateway, that data is first written to the local cache disk on the gateway itself.
- Once the data has been safely persisted to the local cache, only then does the File Gateway acknowledge the write back to the client.
-
From there, File Gateway transfers the data to the S3 bucket asynchronously in the background, optimizing data transfer using multipart parallel uploads, and encrypting data in transit using HTTPS.